wand.image — Image objects¶
Opens and manipulates images. Image objects can be used in with
statement, and these resources will be automatically managed (even if any
error happened):
with Image(filename='pikachu.png') as i:
print('width =', i.width)
print('height =', i.height)
- wand.image.ALPHA_CHANNEL_TYPES = ('undefined', 'activate', 'associate', 'background', 'copy', 'deactivate', 'discrete', 'disassociate', 'extract', 'off', 'on', 'opaque', 'remove', 'set', 'shape', 'transparent')¶
(
tuple) The list ofalpha_channeltypes.'undefined''activate''background''copy''deactivate''discrete'- Only available in ImageMagick-7'extract''off'- Only available in ImageMagick-7'on'- Only available in ImageMagick-7'opaque''reset'- Only available in ImageMagick-6'set''shape''transparent''flatten'- Only available in ImageMagick-6'remove'
See also
- ImageMagick Image Channel
Describes the SetImageAlphaChannel method which can be used to modify alpha channel. Also describes AlphaChannelType
- wand.image.AUTO_THRESHOLD_METHODS = ('undefined', 'kapur', 'otsu', 'triangle')¶
(
tuple) The list of methods used byImage.auto_threshold()'undefined''kapur''otsu''triangle'
New in version 0.5.5.
- class wand.image.ArtifactTree(image)¶
Splay tree to map image artifacts. Values defined here are intended to be used elseware, and will not be written to the encoded image.
For example:
# Omit timestamp from PNG file headers. with Image(filename='input.png') as img: img.artifacts['png:exclude-chunks'] = 'tIME' img.save(filename='output.png')
- Parameters:
image (
Image) – an image instance
Note
You don’t have to use this by yourself. Use
Image.artifactsproperty instead.New in version 0.5.0.
- class wand.image.BaseImage(wand)¶
The abstract base of
Image(container) andSingleImage. That means the most of operations, defined in this abstract class, are possible for bothImageandSingleImage.New in version 0.3.0.
- adaptive_blur(radius=0.0, sigma=0.0, channel=None)¶
Adaptively blurs the image by decreasing Gaussian as the operator approaches detected edges.
- See:
Example of Adaptive Blur.
- Parameters:
radius (
numbers.Real) – size of gaussian aperture.sigma (
numbers.Real) – Standard deviation of the gaussian filter.channel (
basestring) – Apply the blur effect on a specific channel. SeeCHANNELS.
New in version 0.5.3.
Changed in version 0.5.5: Added optional
channelargument
- adaptive_resize(columns=None, rows=None)¶
Adaptively resize image by applying Mesh interpolation.
- Parameters:
columns (
numbers.Integral) – width of resized image.rows (
numbers.Integral) – height of resized image.
New in version 0.5.3.
- adaptive_sharpen(radius=0.0, sigma=0.0, channel=None)¶
Adaptively sharpens the image by sharpening more intensely near image edges and less intensely far from edges.
- See:
Example of Adaptive Sharpen.
- Parameters:
radius (
numbers.Real) – size of gaussian aperture.sigma (
numbers.Real) – Standard deviation of the gaussian filter.channel (
basestring) – Apply the sharpen effect on a specific channel. SeeCHANNELS.
New in version 0.5.3.
Changed in version 0.5.5: Added optional
channelargument
- adaptive_threshold(width, height, offset=0.0)¶
Applies threshold for each pixel based on neighboring pixel values.
- Parameters:
width (
numbers.Integral) – size of neighboring pixels on the X-axis.height (
numbers.Integral) – size of neighboring pixels on the Y-axis.offset (
numbers.Real) – normalized number between 0.0 andquantum_range. Forces the pixels to black if values are belowoffset.
New in version 0.5.3.
- property alpha_channel¶
(
bool) Get state of image alpha channel. It can also be used to enable/disable alpha channel, but with different behavior such as new, copied, or existing.Behavior of setting
alpha_channelis defined with the following values:'activate','on', orTruewill enable an imagesalpha channel. Existing alpha data is preserved.
'deactivate','off', orFalsewill disable an imagesalpha channel. Any data on the alpha will be preserved.
'associate'&'disassociate'toggle alpha channel flag incertain image-file specifications.
'set'enables and resets any data in an images alpha channel.'opaque'enables alpha/matte channel, and forces full opaqueimage.
'transparent'enables alpha/matte channel, and forces fulltransparent image.
'extract'copies data in alpha channel across all other channels,and disables alpha channel.
'copy'calculates the gray-scale of RGB channels,and applies it to alpha channel.
'shape'is identical to'copy', but will color the resultingimage with the value defined with
background_color.
'remove'will compositebackground_colorvalue.'background'replaces full-transparent color with backgroundcolor.
Note
The
alpha_channelattribute will always returnTrueif alpha channel is enabled, andFalseotherwise. Setting this property with a string value fromALPHA_CHANNEL_TYPESwill resolve to aboolafter applying channel operations listed above.With ImageMagick-6, values
'on'&'off'are aliased to'activate'&'deactivate'. However in ImageMagick-7, both'on'&'off'have their own behavior.New in version 0.2.1.
Changed in version 0.4.1: Support for additional setting values. However
Image.alpha_channelwill continue to returnboolif the current alpha/matte state is enabled.Changed in version 0.6.0: Setting the alpha channel will apply the change to all frames in the image stack.
- property animation¶
(
bool) Whether the image is animation or not. It doesn’t only mean that the image has two or more images (frames), but all frames are even the same size. It’s about image format, not content. It’sFalseeven if image/ico consists of two or more images of the same size.For example, it’s
Falsefor image/jpeg, image/gif, image/ico.If image/gif has two or more frames, it’s
True. If image/gif has only one frame, it’sFalse.New in version 0.3.0.
Changed in version 0.3.8: Became to accept image/x-gif as well.
- annotate(text, drawing_wand, left=0, baseline=0, angle=0)¶
Draws text on an image. This method differs from
caption()as it usesDrawingclass to manage the font configuration & style context.from wand.drawing import Drawing from wand.image import Image with Image(filename='input.jpg') as img: with Drawing() as ctx: ctx.font_family = 'Times New Roman, Nimbus Roman No9' ctx.font_size = 18 ctx.text_decoration = 'underline' ctx.text_kerning = -1 img.annotate('Hello World', ctx, left=20, baseline=50) img.save(filename='output.jpg')
- Parameters:
text (
wand.drawing.Drawing) – String to annotate on image.drawing_wand – Font configuration & style context.
left (
numbers.Real) – X-axis offset of the text baseline.baseline (
numbers.Real) – Y-axis offset of the bottom of the text.angle (
numbers.Real) – Degree rotation to draw text at.
New in version 0.5.6.
- property antialias¶
(
bool) If vectors & fonts will use anti-aliasing.Changed in version 0.5.0: Previously named
font_antialias.
- auto_gamma()¶
Adjust the gamma level of an image.
New in version 0.5.4.
- auto_level()¶
Scale the minimum and maximum values to a full quantum range.
New in version 0.5.4.
- auto_orient()¶
Adjusts an image so that its orientation is suitable for viewing (i.e. top-left orientation). If available it uses
MagickAutoOrientImage()(was added in ImageMagick 6.8.9+) if you have an older magick library, it will use_auto_orient()method for fallback.New in version 0.4.1.
- auto_threshold(method='kapur')¶
Automatically performs threshold method to reduce grayscale data down to a binary black & white image. Included algorithms are Kapur, Otsu, and Triangle methods.
Warning
This class method is only available with ImageMagick 7.0.8-41, or greater.
- Parameters:
method (
basestring) – Which threshold method to apply. SeeAUTO_THRESHOLD_METHODS. Defaults to'kapur'.- Raises:
WandLibraryVersionError – if function is not available on system’s library.
New in version 0.5.5.
- property background_color¶
(
wand.color.Color) The image background color. It can also be set to change the background color.New in version 0.1.9.
Changed in version 0.6.7: Allow property to be set before image read.
- black_threshold(threshold)¶
Forces all pixels above a given color as black. Leaves pixels above threshold unaltered.
- Parameters:
threshold (
Color) – Color to be referenced as a threshold.
New in version 0.5.3.
- property blue_primary¶
(
tuple) The chromatic blue primary point for the image. With ImageMagick-6 the primary value is(x, y)coordinates; however, ImageMagick-7 has(x, y, z).New in version 0.5.2.
- blue_shift(factor=1.5)¶
Mutes colors of the image by shifting blue values.
- See:
Example of Blue Shift
- Parameters:
factor (
numbers.Real) – Amount to adjust values.
New in version 0.5.3.
- blur(radius=0.0, sigma=0.0, channel=None)¶
Blurs the image. Convolve the image with a gaussian operator of the given
radiusand standard deviation (sigma). For reasonable results, theradiusshould be larger thansigma. Use aradiusof 0 andblur()selects a suitableradiusfor you.- See:
Example of Blur.
- Parameters:
radius (
numbers.Real) – the radius of the, in pixels, not counting the center pixel. Default is0.0.sigma (
numbers.Real) – the standard deviation of the, in pixels. Default value is0.0.channel (
basestring) – Optional color channel to apply blur. SeeCHANNELS.
New in version 0.4.5.
Changed in version 0.5.5: Added optional
channelargument.Changed in version 0.5.7: Positional arguments
radius&sigmanhave been converted to key-word arguments.
- border(color, width, height, compose='copy')¶
Surrounds the image with a border.
- Parameters:
bordercolor – the border color pixel wand
width (
numbers.Integral) – the border widthheight (
numbers.Integral) – the border heightcompose (
basestring) – Use composite operator when applying frame. Only used if called with ImageMagick 7+.
New in version 0.3.0.
Changed in version 0.5.0: Added
composeparameter, and ImageMagick 7 support.
- property border_color¶
(
wand.color.Color) The image border color. Used for special effects likepolaroid().New in version 0.5.4.
- brightness_contrast(brightness=0.0, contrast=0.0, channel=None)¶
Converts
brightness&contrastparameters into a slope & intercept, and applies a polynomial function.- Parameters:
brightness (
numbers.Real) – between-100.0and100.0. Default is0.0for unchanged.contrast (
numbers.Real) – between-100.0and100.0. Default is0.0for unchanged.channel – Isolate a single color channel to apply contrast. See
CHANNELS.
New in version 0.5.4.
Changed in version 0.5.5: Optional
channelargument added.
- c_clear_exception = wand.api.library.MagickClearException¶
(
ctypes.CFUNCTYPE) Thectypesfunction that clears an exception of theresource.Note
It is an abstract attribute that has to be implemented in the subclass.
- c_destroy_resource = wand.api.library.DestroyMagickWand¶
(
ctypes.CFUNCTYPE) Thectypesfunction that destroys theresource.Note
It is an abstract attribute that has to be implemented in the subclass.
- c_get_exception = wand.api.library.MagickGetException¶
(
ctypes.CFUNCTYPE) Thectypesfunction that gets an exception from theresource.Note
It is an abstract attribute that has to be implemented in the subclass.
- c_is_resource = wand.api.library.IsMagickWand¶
(
ctypes.CFUNCTYPE) Thectypespredicate function that returns whether the given pointer (that contains a resource data usually) is a valid resource.Note
It is an abstract attribute that has to be implemented in the subclass.
- canny(radius=0.0, sigma=1.0, lower_percent=0.1, upper_percent=0.3)¶
Detect edges by leveraging a multi-stage Canny algorithm.
Warning
This class method is only available with ImageMagick 7.0.8-41, or greater.
- Parameters:
radius (
numbers.Real) – Size of gaussian filter.sigma (
numbers.Real) – Standard deviation of gaussian filter.lower_percent (
numbers.Real) – Normalized lower threshold. Values between0.0(0%) and1.0(100%). The default value is0.1or 10%.upper_percent (
numbers.Real) – Normalized upper threshold. Values between0.0(0%) and1.0(100%). The default value is0.3or 30%.
- Raises:
WandLibraryVersionError – if function is not available on system’s library.
New in version 0.5.5.
- caption(text, left=0, top=0, width=None, height=None, font=None, gravity=None)¶
Writes a caption
textinto the position.- Parameters:
text (
basestring) – text to writeleft (
numbers.Integral) – x offset in pixelstop (
numbers.Integral) – y offset in pixelswidth (
numbers.Integral) – width of caption in pixels. default iswidthof the imageheight (
numbers.Integral) – height of caption in pixels. default isheightof the imagefont (
wand.font.Font) – font to use. default isfontof the imagegravity (
basestring) – text placement gravity. uses the currentgravitysetting of the image by default
New in version 0.3.0.
- cdl(ccc)¶
Alias for
color_decision_list().New in version 0.5.7.
- charcoal(radius, sigma)¶
Transform an image into a simulated charcoal drawing.
- See:
Example of Charcoal.
- Parameters:
radius (
numbers.Real) – The size of the Gaussian operator.sigma (
numbers.Real) – The standard deviation of the Gaussian.
New in version 0.5.3.
- chop(width=None, height=None, x=None, y=None, gravity=None)¶
Removes a region of an image, and reduces the image size accordingly.
- Parameters:
width (
numbers.Integral) – Size of region.height (
numbers.Integral) – Size of region.x (
numbers.Integral) – Offset on the X-axis.y (
numbers.Integral) – Offset on the Y-axis.gravity (
basestring) – Helper to auto-calculate offset. SeeGRAVITY_TYPES.
New in version 0.5.5.
Changed in version 0.6.8: Added
gravityargument.Changed in version 0.6.12: Allow zero values for
width&heightarguments.
- clahe(width, height, number_bins, clip_limit)¶
Contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization.
Warning
The CLAHE method is only available with ImageMagick-7.
- Parameters:
width (
numbers.Integral) – Tile division width.height (
numbers.Integral) – Tile division height.number_bins (
numbers.Real) – Histogram bins.clip_limit (
numbers.Real) – contrast limit.
- Raises:
WandLibraryVersionError – If system’s version of ImageMagick does not support this method.
New in version 0.5.5.
- clamp(channel=None)¶
Restrict color values between 0 and quantum range. This is useful when applying arithmetic operations that could result in color values over/under-flowing.
- Parameters:
channel (
basestring) – Optional color channel.
New in version 0.5.0.
Changed in version 0.5.5: Added
channelargument.
- clone()¶
Clones the image. It is equivalent to call
Imagewithimageparameter.with img.clone() as cloned: # manipulate the cloned image pass
- Returns:
the cloned new image
- Return type:
New in version 0.1.1.
- clut(image, method='undefined', channel=None)¶
Replace color values by referencing another image as a Color Look Up Table.
- Parameters:
image (
wand.image.BaseImage) – Color Look Up Table image.method (
basestring) – Pixel Interpolate method. Only available with ImageMagick-7. SeePIXEL_INTERPOLATE_METHODSchannel (
basestring) – Optional color channel to target. SeeCHANNELS
New in version 0.5.0.
Changed in version 0.5.5: Added optional
channelargument.
- coalesce()¶
Rebuilds image sequence with each frame size the same as first frame, and composites each frame atop of previous.
Note
Only affects GIF, and other formats with multiple pages/layers.
New in version 0.5.0.
- color_decision_list(ccc)¶
Applies color correction from a Color Correction Collection (CCC) xml string. An example of xml:
<ColorCorrectionCollection xmlns="urn:ASC:CDL:v1.2"> <ColorCorrection id="cc03345"> <SOPNode> <Slope> 0.9 1.2 0.5 </Slope> <Offset> 0.4 -0.5 0.6 </Offset> <Power> 1.0 0.8 1.5 </Power> </SOPNode> <SATNode> <Saturation> 0.85 </Saturation> </SATNode> </ColorCorrection> </ColorCorrectionCollection>
- Parameters:
ccc (
basestring) – A XML string of the CCC contents.
New in version 0.5.7.
- color_map(index, color=None)¶
Get & Set a color at a palette index. If
coloris given, the color at the index location will be set & returned. Omitting thecolorargument will only return the color value at index.Valid indexes are between
0and totalcolorsof the image.Note
Ensure the image type is set to
'palette'before calling thecolor_map()method. For example:with Image(filename='graph.png') as img: img.type = 'palette' palette = [img.color_map(idx) for idx in range(img.colors)] # ...
- Parameters:
index (
numbers.Integral) – The color position of the image palette.color (
wand.color.Color) – Optional color to _set_ at the given index.
- Returns:
Color at index.
- Return type:
New in version 0.5.3.
- color_matrix(matrix)¶
Adjust color values by applying a matrix transform per pixel.
Matrix should be given as 2D list, with a max size of 6x6.
An example of 3x3 matrix:
matrix = [ [1.0, 0.0, 0.0], [0.0, 1.0, 0.0], [0.0, 0.0, 1.0], ]
Which would translate RGB color channels by calculating the following:
\[\begin{split}\begin{aligned} red' &= 1.0 * red + 0.0 * green + 0.0 * blue\\ green' &= 0.0 * red + 1.0 * green + 0.0 * blue\\ blue' &= 0.0 * red + 0.0 * green + 1.0 * blue\\ \end{aligned}\end{split}\]For RGB colorspace images, the rows & columns are laid out as:
Red
Green
Blue
n/a
Alpha
Offset
Red’
1
0
0
0
0
0
Green’
0
1
0
0
0
0
Blue’
0
0
1
0
0
0
n/a
0
0
0
0
0
0
Alpha’
0
0
0
0
0
0
Offset’
0
0
0
0
0
0
Or for a CMYK colorspace image:
Cyan
Yellow
Magenta
Black
Alpha
Offset
Cyan’
1
0
0
0
0
0
Yellow’
0
1
0
0
0
0
Magenta’
0
0
1
0
0
0
Black’
0
0
0
1
0
0
Alpha’
0
0
0
0
0
0
Offset’
0
0
0
0
0
0
See color-matrix for examples.
- See:
Example of Color Matrix.
- Parameters:
matrix (
collections.abc.Sequence) – 2D List of doubles.
New in version 0.5.3.
- color_threshold(start=None, stop=None)¶
Forces all pixels in color range to white, and all other pixels to black.
Note
This method is only works with ImageMagick-7.0.10, or later.
- Parameters:
start (
wand.color.Color) – Color to begin color range.stop (
wand.color.Color) – Color to end color range.
New in version 0.6.4.
- colorize(color=None, alpha=None)¶
Blends a given fill color over the image. The amount of blend is determined by the color channels given by the
alphaargument.- See:
Example of Colorize.
- Parameters:
color (
wand.color.Color) – Color to paint image with.alpha (
wand.color.Color) – Defines how to blend color.
New in version 0.5.3.
- property colors¶
(
numbers.Integral) Count of unique colors used within the image. This is READ ONLY property.New in version 0.5.3.
- property colorspace¶
(
basestring) The image colorspace.Defines image colorspace as in
COLORSPACE_TYPESenumeration.It may raise
ValueErrorwhen the colorspace is unknown.New in version 0.3.4.
- combine(channel='rgb_channels', colorspace='rgb')¶
Creates an image where each color channel is assigned by a grayscale image in a sequence.
Warning
If your using ImageMagick-6, use
channelargument to control the color-channel order. With ImageMagick-7, thechannelargument has been replaced withcolorspace.For example:
for wand.image import Image with Image() as img: img.read(filename='red_channel.png') img.read(filename='green_channel.png') img.read(filename='blue_channel.png') img.combine(colorspace='rgb') img.save(filename='output.png')
- Parameters:
channel (
basestring) – Determines the colorchannel ordering of the sequence. Only used for ImageMagick-6. SeeCHANNELS.colorspace (
basestring) – Determines the colorchannel ordering of the sequence. Only used for ImageMagick-7. SeeCOLORSPACE_TYPES.
New in version 0.5.9.
- compare(image, metric='undefined', highlight=None, lowlight=None)¶
Compares an image with another, and returns a reconstructed image & computed distortion. The reconstructed image will show the differences colored with
highlight, and similarities withlowlight.If you need the computed distortion between to images without a image being reconstructed, use
get_image_distortion()method.Set
fuzzproperty to adjust pixel-compare thresholds.For example:
from wand.image import Image with Image(filename='input.jpg') as base: with Image(filename='subject.jpg') as img: base.fuzz = base.quantum_range * 0.20 # Threshold of 20% result_image, result_metric = base.compare(img) with result_image: result_image.save(filename='diff.jpg')
- Parameters:
image (
wand.image.Image) – The reference imagemetric (
basestring) – The metric type to use for comparing. SeeCOMPARE_METRICShighlight (
Colororbasestring) – Set the color of the delta pixels in the resulting difference image.lowlight (
Colororbasestring) – Set the color of the similar pixels in the resulting difference image.
- Returns:
The difference image(
wand.image.Image), the computed distortion between the images (numbers.Real)- Return type:
tuple(Image,numbers.Real)
New in version 0.4.3.
Changed in version 0.5.3: Added support for
highlight&lowlight.
- complex(operator='undefined', snr=None)¶
Performs complex mathematics against two images in a sequence, and generates a new image with two results.
from wand.image import Image with Image(filename='real_part.png') as imgA: with Image(filename='imaginary_part.png') as imgB: imgA.sequence.append(imgB) with imgA.complex('conjugate') as results: results.save(filename='output-%02d.png')
Warning
This class method is only available with ImageMagick 7.0.8-41, or greater.
- Parameters:
operator (
basestring) – Define which mathematic operator to perform. SeeCOMPLEX_OPERATORS.snr (
basestring) – OptionalSNRparameter for'divide'operator.
- Raises:
WandLibraryVersionError – If ImageMagick library does not support this function.
New in version 0.5.5.
- property compose¶
(
basestring) The type of image compose. It’s a string fromCOMPOSITE_OPERATORSlist. It also can be set.New in version 0.5.1.
- composite(image, left=None, top=None, operator='over', arguments=None, gravity=None)¶
Places the supplied
imageover the current image, with the top left corner ofimageat coordinatesleft,topof the current image. The dimensions of the current image are not changed.- Parameters:
image (
wand.image.Image) – the image placed over the current imageleft (
numbers.Integral) – the x-coordinate where image will be placedtop (
numbers.Integral) – the y-coordinate where image will be placedoperator (
basestring) – the operator that affects how the composite is applied to the image. available values can be found in theCOMPOSITE_OPERATORSlist. Default is'over'.arguments (
basestring) – Additional numbers given as a geometry string, or comma delimited values. This is needed for'blend','displace','dissolve', and'modulate'operators.gravity – Calculate the
top&leftvalues based on gravity value fromGRAVITY_TYPES.
- Type:
gravity:
basestring
New in version 0.2.0.
Changed in version 0.5.3: The operator can be set, as well as additional composite arguments.
Changed in version 0.5.3: Optional
gravityargument was added.
- composite_channel(channel, image, operator, left=None, top=None, arguments=None, gravity=None)¶
Composite two images using the particular
channel.- Parameters:
channel – the channel type. available values can be found in the
CHANNELSmappingimage (
Image) – the composited source image. (the receiver image becomes the destination)operator (
basestring) – the operator that affects how the composite is applied to the image. available values can be found in theCOMPOSITE_OPERATORSlistleft (
numbers.Integral) – the column offset of the composited source imagetop (
numbers.Integral) – the row offset of the composited source imagearguments (
basestring) – Additional numbers given as a geometry string, or comma delimited values. This is needed for'blend','displace','dissolve', and'modulate'operators.gravity – Calculate the
top&leftvalues based on gravity value fromGRAVITY_TYPES.
- Type:
gravity:
basestring- Raises:
ValueError – when the given
channeloroperatoris invalid
New in version 0.3.0.
Changed in version 0.5.3: Support for optional composite arguments has been added.
Changed in version 0.5.3: Optional
gravityargument was added.
- property compression¶
(
basestring) The type of image compression. It’s a string fromCOMPRESSION_TYPESlist. It also can be set.New in version 0.3.6.
Changed in version 0.5.2: Setting
compressionnow sets both image_info and images in the internal image stack.
- property compression_quality¶
(
numbers.Integral) Compression quality of this image.New in version 0.2.0.
Changed in version 0.5.2: Setting
compression_qualitynow sets both image_info and images in the internal image stack.
- concat(stacked=False)¶
Concatenates images in stack into a single image. Left-to-right by default, top-to-bottom if
stackedis True.- Parameters:
stacked (
bool) – stack images in a column, or in a row (default)
New in version 0.5.0.
- connected_components(**kwargs)¶
Evaluates binary image, and groups connected pixels into objects. This method will also return a list of
ConnectedComponentObjectinstances that will describe an object’s features.from wand.image import Image with Image(filename='objects.gif') as img: objects = img.connected_components() for cc_obj in objects: print("{0._id}: {0.size} {0.offset}".format(cc_obj)) #=> 0: (256, 171) (0, 0) #=> 2: (120, 135) (104, 18) #=> 3: (50, 36) (129, 44) #=> 4: (21, 23) (0, 45) #=> 1: (4, 10) (252, 0)
Warning
This class method is only available with ImageMagick 7.0.8-41, or greater.
Tip
Set
fuzzproperty to increase pixel matching by reducing tolerance of color-value comparisons:from wand.image import Image from wand.version import QUANTUM_RANGE with Image(filename='objects.gif') as img: img.fuzz = 0.1 * QUANTUM_RANGE # 10% objects = img.connected_components()
- Parameters:
angle_threshold (
basestring) – Optional argument that merges any region with an equivalent ellipse smaller than a given value. Requires ImageMagick-7.0.9-24, or greater.area_threshold (
basestring) – Optional argument to merge objects under an area size.background_id (
basestring) – Optional argument to identify which object should be the background. Requires ImageMagick-7.0.9-24, or greater.circularity_threshold (
basestring) – Optional argument that merges any region smaller than value defined as:4*pi*area/perimeter^2. Requires ImageMagick-7.0.9-24, or greater.connectivity (
numbers.Integral) – Either4, or8. A value of4will evaluate each pixels top-bottom, & left-right neighbors. A value of8will use the same pixels as with4, but will also include the four corners of each pixel. Default value of4.diameter_threshold (
basestring) – Optional argument to merge any region under a given value. A region is defined as:sqr(4*area/pi). Requires ImageMagick-7.0.9-24.eccentricity_threshold – Optional argument to merge any region with ellipse eccentricity under a given value. Requires ImageMagick-7.0.9-24, or greater.
keep (
basestring) – Comma separated list of object IDs to isolate, the reset are converted to transparent.keep_colors (
basestring) – Semicolon separated list of objects to keep by their color value. Requires ImageMagick-7.0.9-24, or greater.keep_top (
basestring) – Keeps only the top number of objects by area. Requires ImageMagick-7.0.9-24, or greater.major_axis_threshold (
basestring) – Optional argument to merge any ellipse with a major axis smaller then given value. Requires ImageMagick-7.0.9-24, or greater.mean_color (
bool) – Optional argument. Replace object color with mean color of the source image.minor_axis_threshold (
basestring) – Optional argument to merge any ellipse with a minor axis smaller then given value. Requires ImageMagick-7.0.9-24, or greater.perimeter_threshold – Optional argument to merge any region with a perimeter smaller than the given value. Requires ImageMagick-7.0.9-24, or greater.
remove (
basestring) – Comma separated list of object IDs to ignore, and convert to transparent.remove_colors (
basestring) – Semicolon separated list of objects to remove by there color. Requires ImageMagick-7.0.9-24, or greater.
- Returns:
A list of
ConnectedComponentObject.- Return type:
- Raises:
WandLibraryVersionError – If ImageMagick library does not support this method.
New in version 0.5.5.
Changed in version 0.5.6: Added
mean_color,keep, &removeoptional arguments.Changed in version 0.6.4: Added
angle_threshold,circularity_threshold,diameter_threshold,eccentricity_threshold,keep_colors,major_axis_threshold,minor_axis_threshold,perimeter_threshold, andremove_colorsoptional arguments.
- contrast(sharpen=True)¶
Enhances the difference between lighter & darker values of the image. Set
sharpentoFalseto reduce contrast.- Parameters:
sharpen (
bool) – Increase, or decrease, contrast. Default isTruefor increased contrast.
New in version 0.5.7.
- contrast_stretch(black_point=0.0, white_point=None, channel=None)¶
Enhance contrast of image by adjusting the span of the available colors.
- Parameters:
black_point (
numbers.Real) – black point between 0.0 and 1.0. default is 0.0white_point (
numbers.Real) – white point between 0.0 and 1.0. Defaults to the same value given to theblack_pointargument.channel (
CHANNELS) – optional color channel to apply contrast stretch
- Raises:
ValueError – if
channelis not inCHANNELS
New in version 0.4.1.
Changed in version 0.5.5: The
white_pointargument will now default to the value given by theblack_pointargument.
- convex_hull(background=None)¶
Find the smallest convex polygon, and returns a list of points.
Note
Requires ImageMagick-7.0.10 or greater.
You can pass the list of points directly to
Drawing.polygon()method to draw the convex hull shape on the image.from wand.image import Image from wand.drawing import Drawing with Image(filename='kdf_black.png') as img: points = img.convex_hull() with Drawing() as ctx: ctx.fill_color = 'transparent' ctx.stroke_color = 'red' ctx.polygon(points=points) ctx(img) img.save(filename='kdf_black_convex_hull.png')


- Parameters:
background (
basestringorColor) – Define which color value to evaluate as the background.- Returns:
list of points
- Return type:
New in version 0.6.4.
- crop(left=0, top=0, right=None, bottom=None, width=None, height=None, reset_coords=True, gravity=None)¶
Crops the image in-place.
+--------------------------------------------------+ | ^ ^ | | | | | | top | | | | | | | v | | | <-- left --> +-------------------+ bottom | | | ^ | | | | | <-- width --|---> | | | | | height | | | | | | | | | | | v | | | | +-------------------+ v | | <--------------- right ----------> | +--------------------------------------------------+
- Parameters:
left (
numbers.Integral) – x-offset of the cropped image. default is 0top (
numbers.Integral) – y-offset of the cropped image. default is 0right (
numbers.Integral) – second x-offset of the cropped image. default is thewidthof the image. this parameter andwidthparameter are exclusive each otherbottom (
numbers.Integral) – second y-offset of the cropped image. default is theheightof the image. this parameter andheightparameter are exclusive each otherwidth (
numbers.Integral) – thewidthof the cropped image. default is thewidthof the image. this parameter andrightparameter are exclusive each otherheight (
numbers.Integral) – theheightof the cropped image. default is theheightof the image. this parameter andbottomparameter are exclusive each otherreset_coords (
bool) – optional flag. If set, after the rotation, the coordinate frame will be relocated to the upper-left corner of the new image. By default is True.gravity (
GRAVITY_TYPES) – optional flag. If set, will calculate thetopandleftattributes. This requires bothwidthandheightparameters to be included.
- Raises:
ValueError – when one or more arguments are invalid
Note
If you want to crop the image but not in-place, use slicing operator.
Changed in version 0.4.1: Added
gravityoption. Usinggravityalong withwidth&heightto auto-adjustleft&topattributes.Changed in version 0.1.8: Made to raise
ValueErrorinstead ofIndexErrorfor invalidwidth/heightarguments.New in version 0.1.7.
- cycle_color_map(offset=1)¶
Shift the image color-map by a given offset.
- Parameters:
offset (
numbers.Integral) – number of steps to rotate index by.
New in version 0.5.3.
- decipher(passphrase)¶
Decrypt ciphered pixels into original values.
Note
ImageErrorwill be thrown if the system’s ImageMagick library was compiled without cipher support.- Parameters:
passphrase (
basestring) – the secret passphrase to decrypt with.
New in version 0.6.3.
- deconstruct()¶
Iterates over internal image stack, and adjust each frame size to minimum bounding region of any changes from the previous frame.
New in version 0.5.0.
- property delay¶
(
numbers.Integral) The number of ticks between frames.New in version 0.5.9.
- property depth¶
(
numbers.Integral) The depth of this image.New in version 0.2.1.
- deskew(threshold)¶
Attempts to remove skew artifacts common with most scanning & optical import devices.
- Params threshold:
limit between foreground & background. Use a real number between 0.0 & 1.0 to match CLI’s percent argument.
New in version 0.5.0.
- despeckle()¶
Applies filter to reduce noise in image.
- See:
Example of Despeckle.
New in version 0.5.0.
- property dispose¶
(
basestring) Controls how the image data is handled during animations. Values are fromDISPOSE_TYPESlist, and can also be set.See also
Dispose Images section in
Animation Basicsarticle.New in version 0.5.0.
- distort(method, arguments, best_fit=False, filter=None)¶
Distorts an image using various distorting methods.
from wand.image import Image from wand.color import Color with Image(filename='checks.png') as img: img.virtual_pixel = 'background' img.background_color = Color('green') img.matte_color = Color('skyblue') arguments = (0, 0, 20, 60, 90, 0, 70, 63, 0, 90, 5, 83, 90, 90, 85, 88) img.distort('perspective', arguments) img.save(filename='checks_perspective.png')


Use
virtual_pixel,background_color, andmatte_colorproperties to control the behavior of pixels rendered outside of the image boundaries.Use
interpolate_methodto control how images scale-up.Distortion viewport, and scale, can be defined by using
Image.artifactsdictionary. For example:img.artifacts['distort:viewport'] = '44x44+15+0' img.artifacts['distort:scale'] = '10'
- See:
Additional examples of Distortion.
- Parameters:
method (
basestring) – Distortion method name fromDISTORTION_METHODSarguments (
collections.abc.Sequence) – List of distorting float arguments unique to distortion methodbest_fit (
bool) – Attempt to resize resulting image fit distortion. Defaults Falsefilter (
basestring) – Optional resampling filter used when calculating pixel-value. Defaults to'mitchell', or'lanczos'based on image type & operation.
New in version 0.4.1.
Changed in version 0.6.11: Included filter= parameter.
- edge(radius=0.0)¶
Applies convolution filter to detect edges.
- See:
Example of Edge.
- Parameters:
radius (
numbers.Real) – aperture of detection filter.
New in version 0.5.0.
- emboss(radius=0.0, sigma=0.0)¶
Applies convolution filter against Gaussians filter.
Note
The radius value should be larger than sigma for best results.
- See:
Example of Emboss.
- Parameters:
radius (
numbers.Real) – filter aperture size.sigma (
numbers.Real) – standard deviation.
New in version 0.5.0.
- encipher(passphrase)¶
Encrypt plain pixels into ciphered values.
Note
ImageErrorwill be thrown if the system’s ImageMagick library was compiled without cipher support.- Parameters:
passphrase (
basestring) – the secret passphrase to encrypt with.
New in version 0.6.3.
Changed in version 0.6.8: Fixed C-API call.
- equalize(channel=None)¶
Equalizes the image histogram
- Parameters:
channel (
basestring) – Optional channel. SeeCHANNELS.
New in version 0.3.10.
Changed in version 0.5.5: Added optional
channelargument.
- evaluate(operator=None, value=0.0, channel=None)¶
Apply arithmetic, relational, or logical expression to an image.
Percent values must be calculated against the quantum range of the image:
fifty_percent = img.quantum_range * 0.5 img.evaluate(operator='set', value=fifty_percent)
- See:
Example of Evaluate Expression.
- Parameters:
operator (
EVALUATE_OPS) – Type of operation to calculatevalue (
numbers.Real) – Number to calculate withoperatorchannel (
CHANNELS) – Optional channel to apply operation on.
- Raises:
TypeError – When
valueis not numeric.ValueError – When
operator, orchannelare not defined in constants.
New in version 0.4.1.
- evaluate_images(operator=None)¶
Create a new image by applying arithmetic operation between all images loaded in the image-stack.
For example:
with Image() as img: img.read(filename='first.png') img.read(filename='second.png') with img.evaluate_images('add') as sum: sum.save(filename='sum.png')
- Parameters:
operator (
EVALUATE_OPS) – Type of operation to calculate.
New in version 0.7.0.
- export_pixels(x=0, y=0, width=None, height=None, channel_map='RGBA', storage='char')¶
Export pixel data from a raster image to a list of values.
The
channel_maptells ImageMagick which color channels to export, and what order they should be written as – per pixel. Valid entries forchannel_mapare:'R'- Red channel'G'- Green channel'B'- Blue channel'A'- Alpha channel (0is transparent)'O'- Alpha channel (0is opaque)'C'- Cyan channel'Y'- Yellow channel'M'- Magenta channel'K'- Black channel'I'- Intensity channel (only for grayscale)'P'- Padding
See
STORAGE_TYPESfor a list of validstorageoptions. This tells ImageMagick what type of data it should calculate & write to. For example; a storage type of'char'will write a 8-bit value between 0 ~ 255, a storage type of'short'will write a 16-bit value between 0 ~ 65535, and a'integer'will write a 32-bit value between 0 ~ 4294967295.Note
By default, the entire image will be exported as
'char'storage with each pixel mapping Red, Green, Blue, & Alpha channels.- Parameters:
x (
numbers.Integral) – horizontal starting coordinate of raster.y (
numbers.Integral) – vertical starting coordinate of raster.width (
numbers.Integral) – horizontal length of raster.height (
numbers.Integral) – vertical length of raster.channel_map (
basestring) – a string listing the channel data format for each pixel.storage (
basestring) – what data type each value should be calculated as.
- Returns:
list of values.
- Return type:
New in version 0.5.0.
Changed in version 0.6.11: Update storage type size for “long” & “quantum” values.
- extent(width=None, height=None, x=None, y=None, gravity=None)¶
Adjust the canvas size of the image. Use
x&yto offset the image’s relative placement in the canvas, orgravityhelper for quick position placement.- Parameters:
width (
numbers.Integral) – the target width of the extended image. Default is thewidthof the image.height (
numbers.Integral) – the target height of the extended image. Default is theheightof the image.x (
numbers.Integral) – the x-axis offset of the extended image. Default is 0, and can not be used withgravity.y (
numbers.Integral) – theyoffset of the extended image. Default is 0, and can not be used withgravity.gravity (
basestring) – position of the item extent when not usingx&y. SeeGRAVITY_TYPES.
New in version 0.4.5.
Changed in version 0.6.8: Added
gravityargument.
- features(distance)¶
Calculate directional image features for each color channel. Feature metrics including:
angular second moment
contrast
correlation
variance sum of squares
inverse difference moment
sum average
sum variance
sum entropy
entropy
difference variance
difference entropy
information measures of correlation 1
information measures of correlation 2
maximum correlation coefficient
With each metric containing horizontal, vertical, left & right diagonal values.
from wand.image import Image with Image(filename='rose:') as img: channel_features = img.features(distance=32) for channels, features in channel_features.items(): print(channels) for feature, directions in features.items(): print(' ', feature) for name, value in directions.items(): print(' ', name, value)
- Parameters:
distance (
numbers.Integral) – Define the distance if pixels to calculate.- Returns:
a dict mapping each color channel with a dict of each feature.
- Return type:
New in version 0.5.5.
- fft(magnitude=True)¶
Alias for
forward_fourier_transform().New in version 0.5.7.
- flip()¶
Creates a vertical mirror image by reflecting the pixels around the central x-axis. It manipulates the image in place.
- See:
Example of Flip and flop.
New in version 0.3.0.
- flop()¶
Creates a horizontal mirror image by reflecting the pixels around the central y-axis. It manipulates the image in place.
- See:
Example of Flip and flop.
New in version 0.3.0.
- property font¶
(
wand.font.Font) The current font options.
- property font_path¶
(
basestring) The path of the current font. It also can be set.
- property font_size¶
(
numbers.Real) The font size. It also can be set.
- property format¶
(
basestring) The image format.If you want to convert the image format, just reset this property:
assert isinstance(img, wand.image.Image) img.format = 'png'
It may raise
ValueErrorwhen the format is unsupported.See also
- ImageMagick Image Formats
ImageMagick uses an ASCII string known as magick (e.g.
GIF) to identify file formats, algorithms acting as formats, built-in patterns, and embedded profile types.
New in version 0.1.6.
- forward_fourier_transform(magnitude=True)¶
Performs a discrete Fourier transform. The image stack is replaced with the results. Either a pair of magnitude & phase images, or real & imaginary (HDRI).
from wand.image import Image from wand.version import QUANTUM_RANGE with Image(filename='source.png') as img: img.forward_fourier_transform() img.depth = QUANTUM_RANGE img.save(filename='fft_%02d.png')
See also
Note
ImageMagick must have HDRI support to compute real & imaginary components (i.e.
magnitude=False).- Parameters:
magnitude (
bool) – IfTrue, generate magnitude & phase, else real & imaginary. DefaultTrue
New in version 0.5.5.
- frame(matte=None, width=1, height=1, inner_bevel=0, outer_bevel=0, compose='over')¶
Creates a bordered frame around image. Inner & outer bevel can simulate a 3D effect.
- Parameters:
matte (
wand.color.Color) – color of the framewidth (
numbers.Integral) – total size of frame on x-axisheight (
numbers.Integral) – total size of frame on y-axisinner_bevel (
numbers.Real) – inset shadow lengthouter_bevel (
numbers.Real) – outset highlight lengthcompose (
basestring) – Optional composite operator. Default'over', and only available with ImageMagick-7.
New in version 0.4.1.
Changed in version 0.5.6: Added optional
composeparameter.
- function(function, arguments, channel=None)¶
Apply an arithmetic, relational, or logical expression to an image.
Defaults entire image, but can isolate affects to single color channel by passing
CHANNELSvalue tochannelparameter.Note
Support for function methods added in the following versions of ImageMagick.
'polynomial'>= 6.4.8-8'sinusoid'>= 6.4.8-8'arcsin'>= 6.5.3-1'arctan'>= 6.5.3-1
- See:
Example of Function Expression.
- Parameters:
function (
basestring) – a string listed inFUNCTION_TYPESarguments (
collections.abc.Sequence) – a sequence of doubles to apply againstfunctionchannel (
basestring) – optionalCHANNELS, defaults all
- Raises:
ValueError – when a
function, orchannelis not defined in there respected constantTypeError – if
argumentsis not a sequence
New in version 0.4.1.
- property fuzz¶
(
numbers.Real) The normalized real number between0.0andquantum_range. This property influences the accuracy ofcompare().New in version 0.5.3.
- fx(expression, channel=None)¶
Manipulate each pixel of an image by given expression.
FX will preserver current wand instance, and return a new instance of
Imagecontaining affected pixels.Defaults entire image, but can isolate affects to single color channel by passing
CHANNELSvalue tochannelparameter.See also
The anatomy of FX expressions can be found at http://www.imagemagick.org/script/fx.php
- See:
Example of FX.
- Parameters:
expression (
basestring) – The entire FX expression to applychannel (
CHANNELS) – Optional channel to target.
- Returns:
A new instance of an image with expression applied
- Return type:
New in version 0.4.1.
Changed in version 0.6.9: Will raise
WandRuntimeErrorif method is unable to generate a new image & doesn’t throw an exception.
- gamma(adjustment_value=1.0, channel=None)¶
Gamma correct image.
Specific color channels can be correct individual. Typical values range between 0.8 and 2.3.
- See:
Example of Gamma.
- Parameters:
adjustment_value (
numbers.Real) – value to adjust gamma level. Default 1.0channel (
basestring) – optional channel to apply gamma correction
- Raises:
TypeError – if
gamma_pointis not anumbers.RealValueError – if
channelis not inCHANNELS
New in version 0.4.1.
- gaussian_blur(radius=0.0, sigma=0.0, channel=None)¶
Blurs the image. We convolve the image with a gaussian operator of the given
radiusand standard deviation (sigma). For reasonable results, theradiusshould be larger thansigma. Use aradiusof 0 andblur()selects a suitableradiusfor you.- See:
Example of Gaussian Blur.
- Parameters:
radius (
numbers.Real) – the radius of the, in pixels, not counting the center pixelsigma (
numbers.Real) – the standard deviation of the, in pixelschannel (
basestring) – Optional color channel to target. SeeCHANNELS
New in version 0.3.3.
Changed in version 0.5.5: Added
channelargument.Changed in version 0.5.7: Positional arguments
radius&sigmahave been converted to keyword arguments.
- get_image_distortion(image, metric='undefined')¶
Compares two images, and return the specified distortion metric.
This method is faster than
compare()method as ImageMagick will not need to reconstruct an image.- Parameters:
image (
wand.image.BaseImage) – Image to reference.metric (
basestring) – Compare disortion metric to use. SeeCOMPARE_METRICS.
- Returns:
Computed value of the distortion metric used.
- Return type:
New in version 0.6.6.
- property gravity¶
(
basestring) The text placement gravity used when annotating with text. It’s a string fromGRAVITY_TYPESlist. It also can be set.
- property green_primary¶
(
tuple) The chromatic green primary point for the image. With ImageMagick-6 the primary value is(x, y)coordinates; however, ImageMagick-7 has(x, y, z).New in version 0.5.2.
- hald_clut(image, channel=None)¶
Replace color values by referencing a Higher And Lower Dimension (HALD) Color Look Up Table (CLUT). You can generate a HALD image by using ImageMagick’s hald: protocol.
with Image(filename='rose:') as img: with Image(filename='hald:3') as hald: hald.gamma(1.367) img.hald_clut(hald)
- Parameters:
image (
wand.image.BaseImage) – The HALD color matrix.channel (
basestring) – Optional color channel to target. SeeCHANNELS
New in version 0.5.0.
Changed in version 0.5.5: Added
channelargument.
- property height¶
(
numbers.Integral) The height of this image.
- property histogram¶
(
HistogramDict) The mapping that represents the histogram. Keys areColorobjects, and values are the number of pixels.Tip
True-color photos can have millions of color values. If performance is more valuable than accuracy, remember to
quantize()the image before generating aHistogramDict.- with Image(filename=’hd_photo.jpg’) as img:
img.quantize(255, ‘RGB’, 0, False, False) hist = img.histogram
New in version 0.3.0.
- hough_lines(width, height=None, threshold=40)¶
Identify lines within an image. Use
canny()to reduce image to a binary edge before calling this method.Warning
This class method is only available with ImageMagick 7.0.8-41, or greater.
- Parameters:
width (
numbers.Integral) – Local maxima of neighboring pixels.height (
numbers.Integral) – Local maxima of neighboring pixels.threshold (
numbers.Integral) – Line count to limit. Default to 40.
- Raises:
WandLibraryVersionError – If system’s version of ImageMagick does not support this method.
New in version 0.5.5.
- ift(phase, magnitude=True)¶
Alias for
inverse_fourier_transform().New in version 0.5.7.
- implode(amount=0.0, method='undefined')¶
Creates a “imploding” effect by pulling pixels towards the center of the image.
- See:
Example of Implode.
- Parameters:
amount (
numbers.Real) – Normalized degree of effect between 0.0 & 1.0.method (
basestring) – Which interpolate method to apply to effected pixels. SeePIXEL_INTERPOLATE_METHODSfor a list of options. Only available with ImageMagick-7.
New in version 0.5.2.
- import_pixels(x=0, y=0, width=None, height=None, channel_map='RGB', storage='char', data=None)¶
Import pixel data from a byte-string to the image. The instance of
Imagemust already be allocated with the correct size.The
channel_maptells ImageMagick which color channels to export, and what order they should be written as – per pixel. Valid entries forchannel_mapare:'R'- Red channel'G'- Green channel'B'- Blue channel'A'- Alpha channel (0is transparent)'O'- Alpha channel (0is opaque)'C'- Cyan channel'Y'- Yellow channel'M'- Magenta channel'K'- Black channel'I'- Intensity channel (only for grayscale)'P'- Padding
See
STORAGE_TYPESfor a list of validstorageoptions. This tells ImageMagick what type of data it should calculate & write to. For example; a storage type of'char'will write a 8-bit value between 0 ~ 255, a storage type of'short'will write a 16-bit value between 0 ~ 65535, and a'integer'will write a 32-bit value between 0 ~ 4294967295.Note
By default, the entire image will be exported as
'char'storage with each pixel mapping Red, Green, Blue, & Alpha channels.- Parameters:
x (
numbers.Integral) – horizontal starting coordinate of raster.y (
numbers.Integral) – vertical starting coordinate of raster.width (
numbers.Integral) – horizontal length of raster.height (
numbers.Integral) – vertical length of raster.channel_map (
basestring) – a string listing the channel data format for each pixel.storage (
basestring) – what data type each value should be calculated as.
New in version 0.5.0.
Changed in version 0.6.11: Update storage type size for “long” & “quantum” values.
- property interlace_scheme¶
(
basestring) The interlace used by the image. SeeINTERLACE_TYPES.New in version 0.5.2.
Changed in version 0.6.2: The
interlace_schemeproperty now points to the image. Previously was pointing to theMagickWand.
- property interpolate_method¶
(
basestring) The interpolation method of the image. SeePIXEL_INTERPOLATE_METHODS.New in version 0.5.2.
- inverse_fourier_transform(phase, magnitude=True)¶
Applies the inverse of a discrete Fourier transform. The image stack is replaced with the results. Either a pair of magnitude & phase images, or real & imaginary (HDRI).
from wand.image import Image with Image(filename='magnitude.png') as img: with Image(filename='phase.png') as phase: img.inverse_fourier_transform(phase) img.save(filename='output.png')
See also
Note
ImageMagick must have HDRI support to compute real & imaginary components (i.e.
magnitude=False).- Parameters:
New in version 0.5.5.
- iterator_first()¶
Sets the internal image-stack iterator to the first image. Useful for prepending an image at the start of the stack.
New in version 0.6.2.
- iterator_get()¶
Returns the position of the internal image-stack index.
- Return type:
New in version 0.6.2.
- iterator_last()¶
Sets the internal image-stack iterator to the last image. Useful for appending an image to the end of the stack.
New in version 0.6.2.
- iterator_length()¶
Get the count of images in the image-stack.
- Return type:
New in version 0.6.2.
- iterator_previous()¶
Steps the image-stack index back by one.
- Return type:
New in version 0.6.2.
- iterator_reset()¶
Reset internal image-stack iterator. Useful for iterating over the image-stack without allocating
Sequence.New in version 0.6.2.
- iterator_set(index)¶
Sets the index of the internal image-stack.
- Return type:
New in version 0.6.2.
- kmeans(number_colors=None, max_iterations=100, tolerance=0.01)¶
Reduces the number of colors in an image by applying the K-means clustering algorithm.
Note
Requires ImageMagick-7.0.10-37, or later.
- Parameters:
number_colors (
numbers.Integral) – the target number of colors to use as seeds.max_iterations (
numbers.Integral) – maximum number of iterations needed until convergence. Default100.tolerance (
numbers.Real) – maximum tolerance between distrotion iterations. Default0.01
New in version 0.6.4.
- property kurtosis¶
(
numbers.Real) The kurtosis of the image.Tip
If you want both
kurtosis&skewness, it would be faster to callkurtosis_channel()directly.New in version 0.5.3.
- kurtosis_channel(channel='default_channels')¶
Calculates the kurtosis and skewness of the image.
from wand.image import Image with Image(filename='input.jpg') as img: kurtosis, skewness = img.kurtosis_channel()
- Parameters:
channel (
basestring) – Select which color channel to evaluate. SeeCHANNELS. Default'default_channels'.- Returns:
- Return type:
New in version 0.5.3.
- kuwahara(radius=1.0, sigma=None)¶
Edge preserving noise reduction filter.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kuwahara_filter
If
sigmais not given, the value will be calculated as:sigma = radius - 0.5
To match original algorithm’s behavior, increase
radiusvalue by one:myImage.kuwahara(myRadius + 1, mySigma)
Warning
This class method is only available with ImageMagick 7.0.8-41, or greater.
- See:
Example of Kuwahara.
- Parameters:
radius (
numbers.Real) – Size of the filter aperture.sigma (
numbers.Real) – Standard deviation of Gaussian filter.
- Raises:
WandLibraryVersionError – If system’s version of ImageMagick does not support this method.
New in version 0.5.5.
- label(text, left=None, top=None, font=None, gravity=None, background_color='transparent')¶
Writes a label
textinto the position on top of the existing canvas. This method doesn’t autofit text likecaption(). Useleft&top, orgravity, to position the text.- Parameters:
text (
basestring) – text to write.left (
numbers.Integral) – x offset in pixels.top (
numbers.Integral) – y offset in pixels.font (
wand.font.Font) – font to use. default isfontof the image.gravity (
basestring) – text placement gravity.
New in version 0.6.8.
- property length_of_bytes¶
(
numbers.Integral) The original size, in bytes, of the image read. This will return 0 if the image was modified in a way that would invalidate the original length value.New in version 0.5.4.
- level(black=0.0, white=None, gamma=1.0, channel=None)¶
Adjusts the levels of an image by scaling the colors falling between specified black and white points to the full available quantum range.
If only
blackis given,whitewill be adjusted inward.- See:
Example of Level.
- Parameters:
black (
numbers.Real) – Black point, as a percentage of the system’s quantum range. Defaults to 0.white (
numbers.Real) – White point, as a percentage of the system’s quantum range. Defaults to 1.0.gamma (
numbers.Real) – Optional gamma adjustment. Values > 1.0 lighten the image’s midtones while values < 1.0 darken them.channel (
CHANNELS) – The channel type. Available values can be found in theCHANNELSmapping. IfNone, normalize all channels.
Note
Images may not be affected if the
whitevalue is equal to or less than theblackvalue.New in version 0.4.1.
- level_colors(black_color, white_color, channel=None)¶
Maps given colors to “black” & “white” values.
Warning
This class method is only available with ImageMagick 7.0.8-54, or greater.
- Parameters:
black_color (
Color) – linearly map given color as “black” point.white_color (
Color) – linearly map given color as “white” point.channel (
basestring) – target a specific color-channel to levelize.
- Raises:
WandLibraryVersionError – If system’s version of ImageMagick does not support this method.
New in version 0.5.6.
- levelize(black=0.0, white=None, gamma=1.0, channel=None)¶
Reverse of
level(), this method compresses the range of colors betweenblack&whitevalues.If only
blackis given,whitewill be adjusted inward.Warning
This class method is only available with ImageMagick 7.0.8-41, or greater.
- Parameters:
black (
numbers.Real) – Black point, as a percentage of the system’s quantum range. Defaults to 0.white (
numbers.Real) – White point, as a percentage of the system’s quantum range. Defaults to 1.0.gamma (
numbers.Real) – Optional gamma adjustment. Values > 1.0 lighten the image’s midtones while values < 1.0 darken them.channel (
CHANNELS) – The channel type. Available values can be found in theCHANNELSmapping. IfNone, normalize all channels.
- Raises:
WandLibraryVersionError – If system’s version of ImageMagick does not support this method.
New in version 0.5.5.
- levelize_colors(black_color, white_color, channel=None)¶
Reverse of
level_colors(), and creates a de-contrasting gradient of given colors. This works best with grayscale images.Warning
This class method is only available with ImageMagick 7.0.8-54, or greater.
- Parameters:
black_color (
Color) – tint map given color as “black” point.white_color (
Color) – tint map given color as “white” point.channel (
basestring) – target a specific color-channel to levelize.
- Raises:
WandLibraryVersionError – If system’s version of ImageMagick does not support this method.
New in version 0.5.6.
- linear_stretch(black_point=0.0, white_point=1.0)¶
Enhance saturation intensity of an image.
- Parameters:
black_point (
numbers.Real) – Black point between 0.0 and 1.0. Default 0.0white_point (
numbers.Real) – White point between 0.0 and 1.0. Default 1.0
New in version 0.4.1.
- liquid_rescale(width, height, delta_x=0, rigidity=0)¶
Rescales the image with seam carving, also known as image retargeting, content-aware resizing, or liquid rescaling.
- Parameters:
width (
numbers.Integral) – the width in the scaled imageheight (
numbers.Integral) – the height in the scaled imagedelta_x (
numbers.Real) – maximum seam transversal step. 0 means straight seams. default is 0rigidity (
numbers.Real) – introduce a bias for non-straight seams. default is 0
- Raises:
wand.exceptions.MissingDelegateError – when ImageMagick isn’t configured
--with-lqroption.
Note
This feature requires ImageMagick to be configured
--with-lqroption. Or it will raiseMissingDelegateError:See also
- Seam carving — Wikipedia
The article which explains what seam carving is on Wikipedia.
- local_contrast(radius=10, strength=12.5)¶
Increase light-dark transitions within image.
Warning
This class method is only available with ImageMagick 6.9.3, or greater.
- Parameters:
radius (
numbers.Real) – The size of the Gaussian operator. Default value is10.0.strength (
numbers.Real) – Percentage of blur mask to apply. Values can be between0.0and100with a default of12.5.
New in version 0.5.7.
- property loop¶
(
numbers.Integral) Number of frame iterations. A value of0will loop forever.
- magnify()¶
Quickly double an image in size. This is a convenience method. Use
resize(),resample(), orsample()for more control.New in version 0.5.5.
- property matte_color¶
(
wand.color.Color) The color value of the matte channel. This can also be set.New in version 0.4.1.
- property maxima¶
(
numbers.Real) The maximum quantum value within the image. Value between 0.0 andquantum_rangeTip
If you want both
maxima&minima, it would be faster to callrange_channel()directly.New in version 0.5.3.
- property mean¶
(
numbers.Real) The mean of the image, and have a value between 0.0 andquantum_rangeTip
If you want both
mean&standard_deviation, it would be faster to callmean_channel()directly.New in version 0.5.3.
- mean_channel(channel='default_channels')¶
Calculates the mean and standard deviation of the image.
from wand.image import Image with Image(filename='input.jpg') as img: mean, stddev = img.mean_channel()
- Parameters:
channel (
basestring) – Select which color channel to evaluate. SeeCHANNELS. Default'default_channels'.- Returns:
Tuple of
mean&standard_deviationvalues. Themeanvalue will be between 0.0 &quantum_range- Return type:
New in version 0.5.3.
- mean_shift(width, height, color_distance=0.1)¶
Recalculates pixel value by comparing neighboring pixels within a color distance, and replacing with a mean value. Works best with Gray, YCbCr, YIQ, or YUV colorspaces.
Warning
This class method is only available with ImageMagick 7.0.8-41, or greater.
- Parameters:
width (
numbers.Integral) – Size of the neighborhood window in pixels.height (
numbers.Integral) – Size of the neighborhood window in pixels.color_distance (
numbers.Real) – Include pixel values within this color distance.
- Raises:
WandLibraryVersionError – If system’s version of ImageMagick does not support this method.
New in version 0.5.5.
- merge_layers(method)¶
Composes all the image layers from the current given image onward to produce a single image of the merged layers.
The initial canvas’s size depends on the given ImageLayerMethod, and is initialized using the first images background color. The images are then composited onto that image in sequence using the given composition that has been assigned to each individual image. The method must be set with a value from
IMAGE_LAYER_METHODthat is acceptable to this operation. (See ImageMagick documentation for more details.)- Parameters:
method (
basestring) – the method of selecting the size of the initial canvas.
New in version 0.4.3.
- property minima¶
(
numbers.Real) The minimum quantum value within the image. Value between 0.0 andquantum_rangeTip
If you want both
maxima&minima, it would be faster to callrange_channel()directly.New in version 0.5.3.
- minimum_bounding_box(orientation=None)¶
Find the minimum bounding box within the image. Use properties
fuzz&background_colorto influence bounding box thresholds.from wand.image import Image from wand.drawing import Drawing with Image(filename='kdf_black.png') as img: img.fuzz = img.quantum_range * 0.1 img.background_color = 'black' mbr = img.minimum_bounding_box() with Drawing() as ctx: ctx.fill_color = 'transparent' ctx.stroke_color = 'red' ctx.polygon(points=mbr['points']) ctx.fill_color = 'red' ctx.stroke_color = 'transparent' ctx.text(1, 10, '{0:.4g}°'.format(mbr['angle'])) ctx(img) img.save(filename='kdf_black_mbr.png')

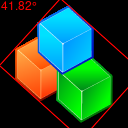
Note
Requires ImageMagick-7.0.10 or later.
- Parameters:
orientation (
basestring) – sets the image orientation. Values can be'landscape', or'portrait'.- Returns:
a directory of MBR properties & corner points.
- Return type:
dict{ “points”:list[tuple(float,float) ], “area”:float, “width”:float, “height”:float, “angle”:float, “unrotate”:float}
New in version 0.6.4.
- mode(width, height=None)¶
Replace each pixel with the mathematical mode of the neighboring colors. This is an alias of the
statistic()method.- Parameters:
width (
numbers.Integral) – Number of neighboring pixels to include in mode.height (
numbers.Integral) – Optional height of neighboring pixels, defaults to the same value aswidth.
New in version 0.5.4.
- modulate(brightness=100.0, saturation=100.0, hue=100.0)¶
Changes the brightness, saturation and hue of an image. We modulate the image with the given
brightness,saturationandhue.- Parameters:
brightness (
numbers.Real) – percentage of brightnesssaturation (
numbers.Real) – percentage of saturationhue (
numbers.Real) – percentage of hue rotation
- Raises:
ValueError – when one or more arguments are invalid
New in version 0.3.4.
- morphology(method=None, kernel=None, iterations=1, channel=None)¶
Manipulate pixels based on the shape of neighboring pixels.
The
methoddetermines what type of effect to apply to matchingkernelshapes. Common methods can be add/remove, or lighten/darken pixel values.The
kerneldescribes the shape of the matching neighbors. Common shapes are provided as “built-in” kernels. See :const`KERNEL_INFO_TYPES` for examples. The format for built-in kernels is:label:geometry
Where label is the kernel name defined in
KERNEL_INFO_TYPES, and :geometry is an optional geometry size. For example:with Image(filename='rose:') as img: img.morphology(method='dilate', kernel='octagon:3x3') # or simply img.morphology(method='edgein', kernel='octagon')
Custom kernels can be applied by following a similar format:
geometry:args
Where geometry is the size of the custom kernel, and args list a comma separated list of values. For example:
custom_kernel='5x3:nan,1,1,1,nan 1,1,1,1,1 nan,1,1,1,nan' with Image(filename='rose:') as img: img.morphology(method='dilate', kernel=custom_kernel)
- Parameters:
method (
basestring) – effect function to apply. SeeMORPHOLOGY_METHODSfor a list of methods.kernel (
basestring) – shape to evaluate surrounding pixels. SeeKERNEL_INFO_TYPESfor a list of built-in shapes.iterations (
numbers.Integral) – Number of times a morphology method should be applied to the image. Default1. Use-1for unlimited iterations until the image is unchanged by the method operator.channel (basestring) – Optional color channel to target. See
CHANNELS
New in version 0.5.0.
Changed in version 0.5.5: Added
channelargument.
- motion_blur(radius=0.0, sigma=0.0, angle=0.0, channel=None)¶
Apply a Gaussian blur along an
angledirection. This simulates motion movement.- See:
Example of Motion Blur.
- Parameters:
radius (
numbers.Real) – Aperture size of the Gaussian operator.sigma (
numbers.Real) – Standard deviation of the Gaussian operator.angle (
numbers.Real) – Apply the effect along this angle.
New in version 0.5.4.
- negate(grayscale=False, channel=None)¶
Negate the colors in the reference image.
- Parameters:
New in version 0.3.8.
- noise(noise_type='uniform', attenuate=1.0, channel=None)¶
Adds noise to image.
- See:
Example of Add Noise.
- Parameters:
noise_type (
basestring) – type of noise to apply. SeeNOISE_TYPES.attenuate (
numbers.Real) – rate of distribution. Only available in ImageMagick-7. Default is1.0.channel (
basestring) – Optionally target a color channel to apply noise to. SeeCHANNELS.
New in version 0.5.3.
Changed in version 0.5.5: Added optional
channelargument.
- normalize(channel=None)¶
Normalize color channels.
- Parameters:
channel (
basestring) – the channel type. available values can be found in theCHANNELSmapping. IfNone, normalize all channels.
- oil_paint(radius=0.0, sigma=0.0)¶
Simulates an oil painting by replace each pixel with most frequent surrounding color.
- Parameters:
radius (
numbers.Real) – The size of the surrounding neighbors.sigma (
numbers.Real) – The standard deviation used by the Gaussian operator. This is only available with ImageMagick-7.
New in version 0.5.4.
- opaque_paint(target=None, fill=None, fuzz=0.0, invert=False, channel=None)¶
Replace any color that matches
targetwithfill. Usefuzzto control the threshold of the target match. Theinvertwill replace all colors but the pixels matching thetargetcolor.- Parameters:
target (
wand.color.Color) – The color to match.fill (
wand.color.Color) – The color to paint with.fuzz (class:numbers.Real) – Normalized real number between 0.0 and
quantum_range. Default is 0.0.invert (
bool) – Replace all colors that do not match target. Default isFalse.channel (
basestring) – Optional color channel to target. SeeCHANNELS
New in version 0.5.4.
Changed in version 0.5.5: Added
channelparameter.
- optimize_layers()¶
Attempts to crop each frame to the smallest image without altering the animation. For best results, call
Image.coalesce()before manipulating any frames. For timing accuracy, anySingleImage.delayoverwrites must be applied after optimizing layers.Note
This will only affect
GIFimage formats.New in version 0.5.0.
- optimize_transparency()¶
Iterates over frames, and sets transparent values for each pixel unchanged by previous frame.
Note
This will only affect
GIFimage formats.New in version 0.5.0.
- options = None¶
(
OptionDict) The mapping of internal option settings.New in version 0.3.0.
Changed in version 0.3.4: Added
'jpeg:sampling-factor'option.Changed in version 0.3.9: Added
'pdf:use-cropbox'option.
- ordered_dither(threshold_map='threshold', channel=None)¶
Executes a ordered-based dither operations based on predetermined threshold maps.
Map
Alias
Description
threshold
1x1
Threshold 1x1 (non-dither)
checks
2x1
Checkerboard 2x1 (dither)
o2x2
2x2
Ordered 2x2 (dispersed)
o3x3
3x3
Ordered 3x3 (dispersed)
o4x4
4x4
Ordered 4x4 (dispersed)
o8x8
8x8
Ordered 8x8 (dispersed)
h4x4a
4x1
Halftone 4x4 (angled)
h6x6a
6x1
Halftone 6x6 (angled)
h8x8a
8x1
Halftone 8x8 (angled)
h4x4o
Halftone 4x4 (orthogonal)
h6x6o
Halftone 6x6 (orthogonal)
h8x8o
Halftone 8x8 (orthogonal)
h16x16o
Halftone 16x16 (orthogonal)
c5x5b
c5x5
Circles 5x5 (black)
c5x5w
Circles 5x5 (white)
c6x6b
c6x6
Circles 6x6 (black)
c6x6w
Circles 6x6 (white)
c7x7b
c7x7
Circles 7x7 (black)
c7x7w
Circles 7x7 (white)
- Parameters:
threshold_map (
basestring) – Name of threshold dither to use, followed by optional arguments.channel (
basestring) – Optional argument to apply dither to specific color channel. SeeCHANNELS.
New in version 0.5.7.
- property orientation¶
(
basestring) The image orientation. It’s a string fromORIENTATION_TYPESlist. It also can be set.New in version 0.3.0.
- property page¶
The dimensions and offset of this Wand’s page as a 4-tuple:
(width, height, x, y).with Image(filename='wizard:') as img: img.page = (595, 842, 0, 0)
Note that since it is based on the virtual canvas, it may not equal the dimensions of an image. See the ImageMagick documentation on the virtual canvas for more information.
This attribute can also be set by using a named papersize. For example:
with Image(filename='wizard:') as img: img.page = 'a4'
New in version 0.4.3.
Changed in version 0.6.4: Added support for setting by papersize.
- property page_height¶
(
numbers.Integral) The height of the page for this wand.New in version 0.4.3.
- property page_width¶
(
numbers.Integral) The width of the page for this wand.New in version 0.4.3.
- property page_x¶
(
numbers.Integral) The X-offset of the page for this wand.New in version 0.4.3.
- property page_y¶
(
numbers.Integral) The Y-offset of the page for this wand.New in version 0.4.3.
- parse_meta_geometry(geometry)¶
Helper method to translate geometry format, and calculate meta-characters against image dimensions.
See “Image Geometry” definitions & examples for more info: https://imagemagick.org/script/command-line-processing.php#geometry
- Parameters:
geometry (
basestring) – user string following ImageMagick’s geometry format.- Returns:
Calculated width, height, offset-x, & offset-y.
- Return type:
- Raises:
ValueError – If given geometry can not be parsed.
New in version 0.5.6.
- percent_escape(string_format)¶
Convenience method that expands ImageMagick’s Percent Escape characters into image attribute values.
with wand.image import Image with Image(filename='tests/assets/sasha.jpg') as img: print(img.percent_escape('%f %wx%h')) #=> sasha.jpg 204x247
Note
Not all percent escaped values can be populated as I/O operations are managed by Python, and not the CLI utility.
- Parameters:
string_format (
basestring) – The prescient escaped string to be translated.- Returns:
String of expanded values.
- Return type:
basestring
New in version 0.5.6.
- polaroid(angle=0.0, caption=None, font=None, method='undefined')¶
Creates a special effect simulating a Polaroid photo.
- See:
Example of Polaroid.
- Parameters:
angle (
numbers.Real) – applies a shadow effect along this angle.caption (
basestring) – Writes a message at the bottom of the photo’s border.font (
wand.font.Font) – Specify font style.method (
basestring) – Interpolation method. ImageMagick-7 only.
New in version 0.5.4.
- polynomial(arguments)¶
Replace image with the sum of all images in a sequence by calculating the pixel values a coefficient-weight value, and a polynomial-exponent.
For example:
with Image(filename='rose:') as img: img.polynomial(arguments=[0.5, 1.0])
The output image will be calculated as:
\[output = 0.5 * image ^ {1.0}\]This can work on multiple images in a sequence by calculating across each frame in the image stack.
with Image(filename='2frames.gif') as img: img.polynomial(arguments=[0.5, 1.0, 0.25, 1.25])
Where the results would be calculated as:
\[output = 0.5 * frame1 ^ {1.0} + 0.25 * frame2 ^ {1.25}\]Warning
This class method is only available with ImageMagick 7.0.8-41, or greater.
- Parameters:
arguments (
collections.abc.Sequence) – A list of real numbers where at least two numbers (weight & exponent) are need for each image in the sequence.- Raises:
WandLibraryVersionError – If system’s version of ImageMagick does not support this method.
New in version 0.5.5.
- posterize(levels=None, dither='no')¶
Reduce color levels per channel.
- Parameters:
levels (
numbers.Integral) – Number of levels per channel.dither (basestring) – Dither method to apply. See
DITHER_METHODS.
New in version 0.5.0.
- quantize(number_colors, colorspace_type='undefined', treedepth=0, dither=False, measure_error=False)¶
quantize analyzes the colors within a sequence of images and chooses a fixed number of colors to represent the image. The goal of the algorithm is to minimize the color difference between the input and output image while minimizing the processing time.
- Parameters:
number_colors (
numbers.Integral) – The target number of colors to reduce the image.colorspace_type (
basestring) – Available value can be found in theCOLORSPACE_TYPES. Defaults value"undefined".treedepth (
numbers.Integral) – A value between0&8where0will allow ImageMagick to calculate the optimal depth withLog4(number_colors). Default value is0.dither (
bool, orbasestring) – Perform dither operation between neighboring pixel values. If using ImageMagick-6, this can be a value ofTrue, orFalse. With ImageMagick-7, use a string fromDITHER_METHODS. DefaultFalse.measure_error (
bool) – Include total quantization error of all pixels in an image & quantized value.
New in version 0.4.2.
Changed in version 0.5.9: Fixed ImageMagick-7
ditherargument, and added keyword defaults.Changed in version 0.7.0: The default value for
colorspace_typeargument is now set to"undefeined"to match CLI behavior.
- property quantum_range¶
(:class:`numbers.Integral) The maximum value of a color channel that is supported by the imagemagick library.
New in version 0.2.0.
- random_threshold(low=0.0, high=1.0, channel=None)¶
Performs a random dither to force a pixel into a binary black & white state. Each color channel operarates independently from each other.
- Parameters:
low (
numbers.Real) – bottom threshold. Any pixel value below the given value will be rendered “0”, or no value. Given threshold value can be between0.0&1.0, or0&quantum_range.high (
numbers.Real) – top threshold. Any pixel value above the given value will be rendered as max quantum value. Given threshold value can be between0.0&1.0, or0&quantum_range.channel (
basestring) – Optional argument to apply dither to specific color channel. SeeCHANNELS.
New in version 0.5.7.
- range_channel(channel='default_channels')¶
Calculate the minimum and maximum of quantum values in image.
from wand.image import Image with Image(filename='input.jpg') as img: minima, maxima = img.range_channel()
- Parameters:
channel (
basestring) – Select which color channel to evaluate. SeeCHANNELS. Default'default_channels'.- Returns:
Tuple of
minima&maximavalues. Each value will be between 0.0 &quantum_range.- Return type:
New in version 0.5.3.
- range_threshold(low_black=0.0, low_white=None, high_white=None, high_black=None)¶
Applies soft & hard thresholding.
For a soft thresholding, parameters should be monotonically increasing:
- with Image(filename=’text.png’) as img:
img.range_threshold(0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8)
For a hard thresholding, parameters should be the same:
- with Image(filename=’text.png’) as img:
img.range_threshold(0.4, 0.4, 0.6, 0.6)
Warning
This class method is only available with ImageMagick 7.0.8-41, or greater.
- Parameters:
low_black (
numbers.Real) – Define the minimum threshold value.low_white (
numbers.Real) – Define the minimum threshold value.high_white (
numbers.Real) – Define the maximum threshold value.high_black (
numbers.Real) – Define the maximum threshold value.
- Raises:
WandLibraryVersionError – If system’s version of ImageMagick does not support this method.
New in version 0.5.5.
- read_mask(clip_mask=None)¶
Sets the read mask where the gray values of the clip mask are used to blend during composite operations. Call this method with a
Noneargument to clear any previously set masks.This method is also useful for
compare()method for limiting region of interest.Warning
This method is only available with ImageMagick-7.
- Parameters:
clip_mask (
BaseImage) – Image to reference as blend mask.
New in version 0.5.7.
- property red_primary¶
(
tuple) The chromatic red primary point for the image. With ImageMagick-6 the primary value is(x, y)coordinates; however, ImageMagick-7 has(x, y, z).New in version 0.5.2.
- region(width=None, height=None, x=None, y=None, gravity=None)¶
Extract an area of the image. This is the same as
crop(), but returns a new instance ofImagewithout altering the original source image.from wand.image import Image with Image(filename='input.jpg') as img: with img.region(width=100, height=100, x=0, y=0) as area: pass
- Parameters:
width (
numbers.Integral) – Area size on the X-axis. Default value is the image’spage_width.height (
numbers.Integral) – Area size on the Y-axis.Default value is the image’spage_height.x (
numbers.Integral) – X-axis offset. This number can be negative. Default value is the image’spage_x.y (
numbers.Integral) – Y-axis offset. This number can be negative. Default value is the image’spage_y.region (
basestring) – Helper attribute to setx&yoffset. SeeGRAVITY_TYPES.
- Returns:
New instance of Wand.
- Return type:
New in version 0.6.8.
- remap(affinity=None, method='no')¶
Rebuild image palette with closest color from given affinity image.
- See:
Example of Remap.
- Parameters:
affinity (
BaseImage) – reference image.method (
basestring) – dither method. SeeDITHER_METHODS. Default is'no'dither.
New in version 0.5.3.
- property rendering_intent¶
(
basestring) PNG rendering intent. SeeRENDERING_INTENT_TYPESfor valid options.New in version 0.5.4.
- resample(x_res=None, y_res=None, filter='undefined', blur=1)¶
Adjust the number of pixels in an image so that when displayed at the given Resolution or Density the image will still look the same size in real world terms.
Note
This method will automatically
coalesce()& resample all frames in a GIF animation. For other image formats,resample()will only effect the current image in the stack. Useiterator_reset()&iterator_next()to traverse the image stack to resample all images in a multi-layer document.with Image(filename='input.tiff') as img: img.iterator_reset() while True: img.resample(128, 128) if not img.iterator_next(): break
- Parameters:
x_res (
numbers.Real) – the X resolution (density) in the scaled image. default is the original resolution.y_res (
numbers.Real) – the Y resolution (density) in the scaled image. default is the original resolution.filter (
basestring,numbers.Integral) – a filter type to use for resizing. choose one inFILTER_TYPES. default is'undefined'which means IM will try to guess best one to use.blur (
numbers.Real) – the blur factor where > 1 is blurry, < 1 is sharp. default is 1
New in version 0.4.5.
- reset_coords()¶
Reset the coordinate frame of the image so to the upper-left corner is (0, 0) again (crop and rotate operations change it).
New in version 0.2.0.
- reset_sequence()¶
Abstract method prototype. See
wand.image.Image.reset_sequence().New in version 0.6.0.
- resize(width=None, height=None, filter='undefined', blur=1)¶
Resizes the image.
- Parameters:
width (
numbers.Integral) – the width in the scaled image. default is the original widthheight (
numbers.Integral) – the height in the scaled image. default is the original heightfilter (
basestring,numbers.Integral) – a filter type to use for resizing. choose one inFILTER_TYPES. default is'undefined'which means IM will try to guess best one to useblur (
numbers.Real) – the blur factor where > 1 is blurry, < 1 is sharp. default is 1
Changed in version 0.2.1: The default value of
filterhas changed from'triangle'to'undefined'instead.Changed in version 0.1.8: The
blurparameter changed to takenumbers.Realinstead ofnumbers.Rational.New in version 0.1.1.
- property resolution¶
(
tuple) Resolution of this image.New in version 0.3.0.
Changed in version 0.5.8: Resolution returns a tuple of float values to match ImageMagick’s behavior.
- roll(x=0, y=0)¶
Shifts all pixels over by an X/Y offset.
- Parameters:
x (
numbers.Integral) – Number of columns to roll over. Negative value will roll pixels from right-to-left, and positive value will roll pixels from left-to-right. Default value:0.y (
numbers.Integral) – Number of rows to roll over. Negative value will roll pixels from bottom-to-top, and positive value will roll pixels from top-to-bottm. Default value:0.
New in version 0.6.8.
- rotate(degree, background=None, reset_coords=True)¶
Rotates the image right. It takes a
backgroundcolor fordegreethat isn’t a multiple of 90.- See:
Example of Rotation.
- Parameters:
degree (
numbers.Real) – a degree to rotate. multiples of 360 affect nothingbackground (
wand.color.Color) – an optional background color. default is transparentreset_coords (
bool) – optional flag. If set, after the rotation, the coordinate frame will be relocated to the upper-left corner of the new image. By default is True.
New in version 0.2.0: The
reset_coordsparameter.New in version 0.1.8.
- rotational_blur(angle=0.0, channel=None)¶
Blur an image in a radius around the center of an image.
Warning
Requires ImageMagick-6.8.8 or greater.
- See:
Example of Rotational Blur.
- Parameters:
angle (
numbers.Real) – Degrees of rotation to blur with.channel (
basestring) – Optional channel to apply the effect against. SeeCHANNELSfor a list of possible values.
- Raises:
WandLibraryVersionError – If system’s version of ImageMagick does not support this method.
New in version 0.5.4.
- sample(width=None, height=None)¶
Resizes the image by sampling the pixels. It’s basically quicker than
resize()except less quality as a trade-off.- Parameters:
width (
numbers.Integral) – the width in the scaled image. default is the original widthheight (
numbers.Integral) – the height in the scaled image. default is the original height
New in version 0.3.4.
- property sampling_factors¶
(
tuple) Factors used in sampling data streams. This can be set by given it a string"4:2:2", or tuple of numbers(2, 1, 1). However the given string value will be parsed to aspect ratio (i.e."4:2:2"internally becomes"2,1").Note
This property is only used by YUV, DPX, & EXR encoders. For JPEG & TIFF set
"jpeg:sampling-factor"onImage.optionsdictionary:with Image(filename='input.jpg') as img: img.options['jpeg:sampling-factor'] = '2x1'
New in version 0.6.3.
- scale(columns=1, rows=1)¶
Increase image size by scaling each pixel value by given
columnsandrows.- Parameters:
columns (
numbers.Integral) – The number of columns, in pixels, to scale the image horizontally.rows (
numbers.Integral) – The number of rows, in pixels, to scale the image vertically.
New in version 0.5.7.
- property scene¶
(
numbers.Integral) The scene number of the current frame within an animated image.New in version 0.5.4.
- property seed¶
(
numbers.Integral) The seed for random number generator.Warning
This property is only available with ImageMagick 7.0.8-41, or greater.
New in version 0.5.5.
- selective_blur(radius=0.0, sigma=0.0, threshold=0.0, channel=None)¶
Blur an image within a given threshold.
For best effects, use a value between 10% and 50% of
quantum_rangefrom wand.image import Image with Image(filename='photo.jpg') as img: # Apply 8x3 blur with a 10% threshold img.selective_blur(8.0, 3.0, 0.1 * img.quantum_range)
- See:
Example of Selective Blur.
- Parameters:
radius (
numbers.Real) – Size of gaussian aperture.sigma (
numbers.Real) – Standard deviation of gaussian operator.threshold (
numbers.Real) – Only pixels within contrast threshold are effected. Value should be between0.0andquantum_range.channel (
basestring) – Optional color channel to target. SeeCHANNELS
New in version 0.5.3.
Changed in version 0.5.5: Added
channelargument.
- sepia_tone(threshold=0.8)¶
Creates a Sepia Tone special effect similar to a darkroom chemical toning.
- See:
Example of Sepia Tone.
- Parameters:
threshold (
numbers.Real) – The extent of the toning. Value can be between0&quantum_range, or0&1.0. Default value is0.8or “80%”.
New in version 0.5.7.
- sequence = None¶
(
collections.abc.Sequence) The list ofSingleImages that the image contains.New in version 0.3.0.
- shade(gray=False, azimuth=0.0, elevation=0.0)¶
Creates a 3D effect by simulating a light from an elevated angle.
- See:
Example of Shade.
- Parameters:
gray (
bool) – Isolate the effect on pixel intensity. Default is False.azimuth (
numbers.Real) – Angle from x-axis.elevation (
numbers.Real) – Amount of pixels from the z-axis.
New in version 0.5.0.
- shadow(alpha=0.0, sigma=0.0, x=0, y=0)¶
Generates an image shadow.
- Parameters:
alpha (
numbers.Real) – Ratio of transparency.sigma (
numbers.Real) – Standard deviation of the gaussian filter.x (
numbers.Integral) – x-offset.y (
numbers.Integral) – y-offset.
New in version 0.5.0.
- sharpen(radius=0.0, sigma=0.0, channel=None)¶
Applies a gaussian effect to enhance the sharpness of an image.
Note
For best results, ensure
radiusis larger thansigma.Defaults values of zero will have ImageMagick attempt to auto-select suitable values.
- See:
Example of Sharpen.
- Parameters:
radius (
numbers.Real) – size of gaussian aperture.sigma (
numbers.Real) – Standard deviation of the gaussian filter.channel (
basestring) – Optional color channel to target. SeeCHANNELS.
New in version 0.5.0.
Changed in version 0.5.5: Added
channelargument.
- shave(columns=0, rows=0)¶
Remove pixels from the edges.
- Parameters:
columns (
numbers.Integral) – amount to shave off both sides of the x-axis.rows (
numbers.Integral) – amount to shave off both sides of the y-axis.
New in version 0.5.0.
- shear(background='WHITE', x=0.0, y=0.0)¶
Shears the image to create a parallelogram, and fill the space created with a
backgroundcolor.- Parameters:
background (
wand.color.Color) – Color to fill the void created by shearing the image.x (
numbers.Real) – Slide the image along the X-axis.y (
numbers.Real) – Slide the image along the Y-axis.
New in version 0.5.4.
- sigmoidal_contrast(sharpen=True, strength=0.0, midpoint=0.0, channel=None)¶
Modifies the contrast of the image by applying non-linear sigmoidal algorithm.
with Image(filename='photo.jpg') as img: img.sigmoidal_contrast(sharpen=True, strength=3, midpoint=0.65 * img.quantum_range)
- Parameters:
sharpen (
bool) – Increase the contrast whenTrue(default), else reduces contrast.strength (
numbers.Real) – How much to adjust the contrast. Where a value of0.0has no effect,3.0is typical, and20.0is extreme.midpoint (
numbers.Real) – Normalized value between 0.0 &quantum_rangechannel (
basestring) – Optional color channel to target. SeeCHANNELS.
New in version 0.5.4.
Changed in version 0.5.5: Added
channelargument.
- property signature¶
(
str) The SHA-256 message digest for the image pixel stream.New in version 0.1.9.
- similarity(reference, threshold=0.0, metric='undefined')¶
Scan image for best matching
referenceimage, and return location & similarity.Use parameter
thresholdto stop subimage scanning if the matching similarity value is below the given value. This is the same as the CLI-similarity-thresholdoption.This method will always return a location & the lowest computed similarity value. Users are responsible for checking the similarity value to determine if a matching location is valid. Traditionally, a similarity value greater than 0.3183099 is considered dissimilar.
from wand.image import Image dissimilarity_threshold = 0.318 similarity_threshold = 0.05 with Image(filename='subject.jpg') as img: with Image(filename='object.jpg') as reference: location, diff = img.similarity(reference, similarity_threshold) if diff > dissimilarity_threshold: print('Images too dissimilar to match') elif diff <= similarity_threshold: print('First match @ {left}x{top}'.format(**location)) else: print('Best match @ {left}x{top}'.format(**location))
Warning
This operation can be slow to complete.
- Parameters:
reference (
wand.image.Image) – Image to search for.threshold (
numbers.Real) – Stop scanning if reference similarity is below given threshold. Value can be between0.0andquantum_range. Default is0.0.metric (
basestring) – specify which comparison algorithm to use. SeeCOMPARE_METRICSfor a list of values. Only used by ImageMagick-7.
- Returns:
List of location & similarity value. Location being a dictionary of
width,height,left, &top. The similarity value is the compare distance, so a value of0.0means an exact match.- Return type:
New in version 0.5.4: has been added.
- property size¶
(
tuple) The pair of (width,height).Note
When working with animations, or other layer-based image formats, the
width&heightproperties are referencing the last frame read into the image stack. To get thesizeof the entire animated images, callImage.coalesce()method immediately after reading the image.
- sketch(radius=0.0, sigma=0.0, angle=0.0)¶
Simulates a pencil sketch effect. For best results,
radiusvalue should be larger thansigma.- See:
Example of Sketch.
- Parameters:
radius (
numbers.Real) – size of Gaussian aperture.sigma (
numbers.Real) – standard deviation of the Gaussian operator.angle (
numbers.Real) – direction of blur.
New in version 0.5.3.
- property skewness¶
(
numbers.Real) The skewness of the image.Tip
If you want both
kurtosis&skewness, it would be faster to callkurtosis_channel()directly.New in version 0.5.3.
- smush(stacked=False, offset=0)¶
Appends all images together. Similar behavior to
concat(), but with an optional offset between images.- Parameters:
stacked (
bool) – If True, will join top-to-bottom. If False, join images from left-to-right (default).offset (
numbers.Integral) – Minimum space (in pixels) between each join.
New in version 0.5.3.
- solarize(threshold=0.0, channel=None)¶
Simulates extreme overexposure.
- See:
Example of Solarize.
- Parameters:
threshold (
numbers.Real) – between0.0andquantum_range.channel (
basestring) – Optional color channel to target. SeeCHANNELS
New in version 0.5.3.
Changed in version 0.5.5: Added
channelargument.
- sparse_color(method, colors, channel_mask=7)¶
Interpolates color values between points on an image.
The
colorsargument should be a dict mappingColorkeys to coordinate tuples.For example:
from wand.color import Color from wand.image import Image colors = { Color('RED'): (10, 50), Color('YELLOW'): (174, 32), Color('ORANGE'): (74, 123) } with Image(filename='input.png') as img: img.sparse_color('bilinear', colors)
The available interpolate methods are:
'barycentric''bilinear''shepards''voronoi''inverse''manhattan'
You can control which color channels are effected by building a custom channel mask. For example:
from wand.image import Image, CHANNELS with Image(filename='input.png') as img: colors = { img[50, 50]: (50, 50), img[100, 50]: (100, 50), img[50, 75]: (50, 75), img[100, 100]: (100, 100) } # Only apply Voronoi to Red & Alpha channels mask = CHANNELS['red'] | CHANNELS['alpha'] img.sparse_color('voronoi', colors, channel_mask=mask)
- Parameters:
method (
basestring) – Interpolate method. SeeSPARSE_COLOR_METHODScolors (
abc.Mapping{Color: (int, int) }) – A dictionary ofColorkeys mapped to an (x, y) coordinate tuple.channel_mask (
numbers.Integral) – Isolate specific color channels to apply interpolation. Default to RGB channels.
New in version 0.5.3.
- splice(width=None, height=None, x=None, y=None, gravity=None)¶
Partitions image by splicing a
widthxheightrectangle at (x,y) offset coordinate. The space inserted will be replaced by thebackground_colorvalue.- Parameters:
width (
numbers.Integral) – number of pixel columns.height (
numbers.Integral) – number of pixel rows.x (
numbers.Integral) – offset on the X-axis.y (
numbers.Integral) – offset on the Y-axis.
New in version 0.5.3.
- spread(radius=0.0, method='undefined')¶
Randomly displace pixels within a defined radius.
- See:
Example of Spread.
- Parameters:
radius (
numbers.Real) – Distance a pixel can be displaced from source. Default value is0.0, which will allow ImageMagick to auto select a radius.method – Interpolation method. Only available with ImageMagick-7. See
PIXEL_INTERPOLATE_METHODS.
New in version 0.5.3.
Changed in version 0.5.7: Added default value to
radius.
- property standard_deviation¶
(
numbers.Real) The standard deviation of the image.Tip
If you want both
mean&standard_deviation, it would be faster to callmean_channel()directly.New in version 0.5.3.
- statistic(stat='undefined', width=None, height=None, channel=None)¶
Replace each pixel with the statistic results from neighboring pixel values. The
width&heightdefines the size, or aperture, of the neighboring pixels.- See:
Example of Statistic.
- Parameters:
stat (
basestring) – The type of statistic to calculate. SeeSTATISTIC_TYPES.width (
numbers.Integral) – The size of neighboring pixels on the X-axis.height (
numbers.Integral) – The size of neighboring pixels on the Y-axis.channel (
basestring) – Optional color channel to target. SeeCHANNELS
New in version 0.5.3.
Changed in version 0.5.5: Added optional
channelargument.
- stegano(watermark, offset=0)¶
Hide a digital watermark of an image within the image.
from wand.image import Image # Embed watermark with Image(filename='source.png') as img: with Image(filename='gray_watermark.png') as watermark: print('watermark size (for recovery)', watermark.size) img.stegano(watermark) img.save(filename='public.png') # Recover watermark with Image(width=w, height=h, pseudo='stegano:public.png') as img: img.save(filename='recovered_watermark.png')
- Parameters:
watermark (
wand.image.Image) – Image to hide within image.offset (
numbers.Integral) – Start embedding image after a number of pixels.
New in version 0.5.4.
- strip()¶
Strips an image of all profiles and comments.
New in version 0.2.0.
- swirl(degree=0.0, method='undefined')¶
Swirls pixels around the center of the image. The larger the degree the more pixels will be effected.
- See:
Example of Swirl.
- Parameters:
degree (
numbers.Real) – Defines the amount of pixels to be effected. Value between-360.0and360.0.method (
basestring) – Controls interpolation of the effected pixels. Only available for ImageMagick-7. SeePIXEL_INTERPOLATE_METHODS.
New in version 0.5.7.
- texture(tile)¶
Repeat tile-image across the width & height of the image.
from wand.image import Image with Image(width=100, height=100) as canvas: with Image(filename='tile.png') as tile: canvas.texture(tile) canvas.save(filename='output.png')
- Parameters:
tile (
Image) – image to repeat across canvas.
New in version 0.5.4.
- threshold(threshold=0.5, channel=None)¶
Changes the value of individual pixels based on the intensity of each pixel compared to threshold. The result is a high-contrast, two color image. It manipulates the image in place.
- Parameters:
threshold (
numbers.Real) – threshold as a factor of quantum. A normalized float between0.0and1.0.channel (
basestring) – the channel type. available values can be found in theCHANNELSmapping. IfNone, threshold all channels.
New in version 0.3.10.
- thumbnail(width=None, height=None)¶
Changes the size of an image to the given dimensions and removes any associated profiles. The goal is to produce small low cost thumbnail images suited for display on the web.
- Parameters:
width (
numbers.Integral) – the width in the scaled image. default is the original widthheight (
numbers.Integral) – the height in the scaled image. default is the original height
New in version 0.5.4.
- property ticks_per_second¶
(
numbers.Integral) Internal clock for animated images. .. versionadded:: 0.5.4
- tint(color=None, alpha=None)¶
Applies a color vector to each pixel in the image.
- See:
Example of Tint.
- Parameters:
New in version 0.5.3.
- transform(crop='', resize='')¶
Transforms the image using
MagickTransformImage(), which is a convenience function accepting geometry strings to perform cropping and resizing. Cropping is performed first, followed by resizing. Either or both arguments may be omitted or given an empty string, in which case the corresponding action will not be performed. Geometry specification strings are defined as follows:A geometry string consists of a size followed by an optional offset. The size is specified by one of the options below, where bold terms are replaced with appropriate integer values:
- scale
% Height and width both scaled by specified percentage.
- scale-x
%xscale-y% Height and width individually scaled by specified percentages. Only one % symbol is needed.
- width
Width given, height automagically selected to preserve aspect ratio.
xheightHeight given, width automagically selected to preserve aspect ratio.
- width
xheight Maximum values of width and height given; aspect ratio preserved.
- width
xheight! Width and height emphatically given; original aspect ratio ignored.
- width
xheight> Shrinks images with dimension(s) larger than the corresponding width and/or height dimension(s).
- width
xheight< Enlarges images with dimensions smaller than the corresponding width and/or height dimension(s).
- area
@ Resize image to have the specified area in pixels. Aspect ratio is preserved.
- X
:Y Resize at a given aspect ratio. Common aspect ratios may include
4:3for video/tv,3:2for 35mm film,16:9for HDTV, and2.39:1for cinema. Aspect ratio can be used with the crop parameter, but is only available with ImageMagick version 7.0.8 or greater.
The offset, which only applies to the cropping geometry string, is given by
{+-}x{+-}y, that is, one plus or minus sign followed by an x offset, followed by another plus or minus sign, followed by a y offset. Offsets are in pixels from the upper left corner of the image. Negative offsets will cause the corresponding number of pixels to be removed from the right or bottom edge of the image, meaning the cropped size will be the computed size minus the absolute value of the offset.For example, if you want to crop your image to 300x300 pixels and then scale it by 2x for a final size of 600x600 pixels, you can call:
image.transform('300x300', '200%')
This method is a fairly thin wrapper for the C API, and does not perform any additional checking of the parameters except insofar as verifying that they are of the correct type. Thus, like the C API function, the method is very permissive in terms of what it accepts for geometry strings; unrecognized strings and trailing characters will be ignored rather than raising an error.
- Parameters:
crop (
basestring) – A geometry string defining a subregion of the image to crop toresize (
basestring) – A geometry string defining the final size of the image
See also
- ImageMagick Geometry Specifications
Cropping and resizing geometry for the
transformmethod are specified according to ImageMagick’s geometry string format. The ImageMagick documentation provides more information about geometry strings.
New in version 0.2.2.
- scale
- transform_colorspace(colorspace_type)¶
Transform image’s colorspace.
- Parameters:
colorspace_type (
basestring) – colorspace_type. available value can be found in theCOLORSPACE_TYPES
New in version 0.4.2.
- transparent_color(color, alpha, fuzz=0, invert=False)¶
Makes the color
colora transparent color with a tolerance of fuzz. Thealphaparameter specify the transparency level and the parameterfuzzspecify the tolerance.- Parameters:
color (
wand.color.Color) – The color that should be made transparent on the image, color objectalpha (
numbers.Real) – the level of transparency: 1.0 is fully opaque and 0.0 is fully transparent.fuzz (
numbers.Real) – By default target must match a particular pixel color exactly. However, in many cases two colors may differ by a small amount. The fuzz member of image defines how much tolerance is acceptable to consider two colors as the same. For example, set fuzz to 10 and the color red at intensities of 100 and 102 respectively are now interpreted as the same color for the color.invert (
bool) – Boolean to tell to paint the inverse selection.
New in version 0.3.0.
Changed in version 0.6.3: Parameter
fuzztype switched from Integral to Real.
- transparentize(transparency)¶
Makes the image transparent by subtracting some percentage of the black color channel. The
transparencyparameter specifies the percentage.- Parameters:
transparency (
numbers.Real) – the percentage fade that should be performed on the image, from 0.0 to 1.0
New in version 0.2.0.
- transpose()¶
Creates a vertical mirror image by reflecting the pixels around the central x-axis while rotating them 90-degrees.
New in version 0.4.1.
- transverse()¶
Creates a horizontal mirror image by reflecting the pixels around the central y-axis while rotating them 270-degrees.
New in version 0.4.1.
- trim(color=None, fuzz=0.0, reset_coords=False, percent_background=None, background_color=None)¶
Remove solid border from image. Uses top left pixel as a guide by default, or you can also specify the
colorto remove.- Parameters:
color (
Color) – the border color to remove. if it’s omitted top left pixel is used by defaultfuzz (
numbers.Real) – Defines how much tolerance is acceptable to consider two colors as the same. Value can be between0.0, andquantum_range.reset_coords (
bool) – Reset coordinates after trimming image. DefaultFalse.percent_background (
numbers.Real) – Sets how aggressive the trim operation will be. A value of 0.0 will trim to the minimal bounding box of all matching color, and 1.0 to the most outer edge.background_color – Local alias to
background_color, and has the same effect as definingcolorparameter – but much faster.
New in version 0.2.1.
Changed in version 0.3.0: Optional
colorandfuzzparameters.Changed in version 0.5.2: The
colorparameter may accept color-compliant strings.Changed in version 0.6.0: Optional
reset_coordsparameter added.Changed in version 0.6.4: Optional
percent_background&background_colorparameters have been added.
- property type¶
(
basestring) The image type.Defines image type as in
IMAGE_TYPESenumeration.It may raise
ValueErrorwhen the type is unknown.New in version 0.2.2.
- unique_colors()¶
Discards all duplicate pixels, and rebuilds the image as a single row.
New in version 0.5.0.
- property units¶
(
basestring) The resolution units of this image.
- unsharp_mask(radius=0.0, sigma=1.0, amount=1.0, threshold=0.0, channel=None)¶
Sharpens the image using unsharp mask filter. We convolve the image with a Gaussian operator of the given
radiusand standard deviation (sigma). For reasonable results,radiusshould be larger thansigma. Use a radius of 0 andunsharp_mask()selects a suitable radius for you.- See:
Example of Unsharp Mask.
- Parameters:
radius (
numbers.Real) – the radius of the Gaussian, in pixels, not counting the center pixelsigma (
numbers.Real) – the standard deviation of the Gaussian, in pixelsamount (
numbers.Real) – the percentage of the difference between the original and the blur image that is added back into the originalthreshold (
numbers.Real) – the threshold in pixels needed to apply the difference amount.channel (
basestring) – Optional color channel to target. SeeCHANNELS
New in version 0.3.4.
Changed in version 0.5.5: Added optional
channelargument.Changed in version 0.5.7: Added default values to match CLI behavior.
- vignette(radius=0.0, sigma=0.0, x=0, y=0)¶
Creates a soft vignette style effect on the image.
- See:
Example of Vignette.
- Parameters:
radius (
numbers.Real) – the radius of the Gaussian blur effect.sigma (
numbers.Real) – the standard deviation of the Gaussian effect.x (
numbers.Integral) – Number of pixels to offset inward from the top & bottom of the image before drawing effect.y (
numbers.Integral) – Number of pixels to offset inward from the left & right of the image before drawing effect.
New in version 0.5.2.
- property virtual_pixel¶
(
basestring) The virtual pixel of image. This can also be set with a value fromVIRTUAL_PIXEL_METHOD… versionadded:: 0.4.1
- property wand¶
Internal pointer to the MagickWand instance. It may raise
ClosedImageErrorwhen the instance has destroyed already.
- watermark(image, transparency=0.0, left=0, top=0)¶
Transparentized the supplied
imageand places it over the current image, with the top left corner ofimageat coordinatesleft,topof the current image. The dimensions of the current image are not changed.- Parameters:
image (
wand.image.Image) – the image placed over the current imagetransparency (
numbers.Real) – the percentage fade that should be performed on the image, from 0.0 to 1.0left (
numbers.Integral) – the x-coordinate where image will be placedtop (
numbers.Integral) – the y-coordinate where image will be placed
New in version 0.2.0.
- wave(amplitude=0.0, wave_length=0.0, method='undefined')¶
Creates a ripple effect within the image.
- See:
Example of Wave.
- Parameters:
amplitude (
numbers.Real) – height of wave form.wave_length (
numbers.Real) – width of wave form.method (
basestring) – pixel interpolation method. Only available with ImageMagick-7. SeePIXEL_INTERPOLATE_METHODS
New in version 0.5.2.
- wavelet_denoise(threshold=0.0, softness=0.0)¶
Removes noise by applying a wavelet transform.
Warning
This class method is only available with ImageMagick 7.0.8-41, or greater.
- See:
Example of Wavelet Denoise.
- Parameters:
threshold (
numbers.Real) – Smoothing limit.softness (
numbers.Real) – Attenuate of the smoothing threshold.
- Raises:
WandLibraryVersionError – If system’s version of ImageMagick does not support this method.
New in version 0.5.5.
- white_balance()¶
Uses LAB colorspace to apply a white balance to the image.
Note
Requires ImageMagick-7.0.10-37 or later.
New in version 0.6.4.
- property white_point¶
(
tuple) The chromatic white point for the image. With ImageMagick-6 the primary value is(x, y)coordinates; however, ImageMagick-7 has(x, y, z).New in version 0.5.2.
- white_threshold(threshold)¶
Forces all pixels above a given color as white. Leaves pixels below threshold unaltered.
- Parameters:
threshold (
Color) – Color to be referenced as a threshold.
New in version 0.5.2.
- property width¶
(
numbers.Integral) The width of this image.
- write_mask(clip_mask=None)¶
Sets the write mask which prevents pixel-value updates to the image. Call this method with a
Noneargument to clear any previously set masks.Warning
This method is only available with ImageMagick-7.
- Parameters:
clip_mask (
BaseImage) – Image to reference as blend mask.
New in version 0.5.7.
- wand.image.CHANNELS = {'all_channels': 134217727, 'alpha': 16, 'black': 8, 'blue': 4, 'composite_channels': 31, 'cyan': 1, 'default_channels': 134217727, 'gray': 1, 'gray_channels': 1, 'green': 2, 'index': 32, 'magenta': 2, 'meta': 256, 'opacity': 16, 'readmask': 64, 'red': 1, 'rgb': 7, 'rgb_channels': 7, 'sync_channels': 131072, 'true_alpha': 256, 'undefined': 0, 'write_mask': 128, 'yellow': 4}¶
(
dict) The dictionary of channel types.'undefined''red''gray''cyan''green''magenta''blue''yellow''alpha''opacity''black''index''composite_channels''all_channels''sync_channels''default_channels'
See also
- ImageMagick Color Channels
Lists the various channel types with descriptions of each
Changed in version 0.5.5: Deprecated
true_alpha,rgb_channels, andgray_channelsvalues in favor of MagickCore channel parser.
- wand.image.COLORSPACE_TYPES = ('undefined', 'cmy', 'cmyk', 'gray', 'hcl', 'hclp', 'hsb', 'hsi', 'hsl', 'hsv', 'hwb', 'lab', 'lch', 'lchab', 'lchuv', 'log', 'lms', 'luv', 'ohta', 'rec601ycbcr', 'rec709ycbcr', 'rgb', 'scrgb', 'srgb', 'transparent', 'xyy', 'xyz', 'ycbcr', 'ycc', 'ydbdr', 'yiq', 'ypbpr', 'yuv')¶
(
tuple) The list of colorspaces.'undefined''rgb''gray''transparent''ohta''lab''xyz''ycbcr''ycc''yiq''ypbpr''yuv''cmyk''srgb''hsb''hsl''hwb''rec601luma'- Only available with ImageMagick-6'rec601ycbcr''rec709luma'- Only available with ImageMagick-6'rec709ycbcr''log''cmy''luv''hcl''lch''lms''lchab''lchuv''scrgb''hsi''hsv''hclp''xyy'- Only available with ImageMagick-7'ydbdr'
See also
- ImageMagick Color Management
Describes the ImageMagick color management operations
New in version 0.3.4.
- wand.image.COMPARE_METRICS = ('undefined', 'absolute', 'fuzz', 'mean_absolute', 'mean_error_per_pixel', 'mean_squared', 'normalized_cross_correlation', 'peak_absolute', 'peak_signal_to_noise_ratio', 'perceptual_hash', 'root_mean_square', 'structural_similarity', 'structural_dissimilarity')¶
(
tuple) The list of compare metric types used byImage.compare()andImage.similarity()methods.'undefined''absolute''fuzz''mean_absolute''mean_error_per_pixel''mean_squared''normalized_cross_correlation''peak_absolute''peak_signal_to_noise_ratio''perceptual_hash'- Available with ImageMagick-7'root_mean_square''structural_similarity'- Available with ImageMagick-7'structural_dissimilarity'- Available with ImageMagick-7
See also
New in version 0.4.3.
Changed in version 0.5.4: - Remapped
MetricTypeenum.
- wand.image.COMPOSITE_OPERATORS = ('undefined', 'alpha', 'atop', 'blend', 'blur', 'bumpmap', 'change_mask', 'clear', 'color_burn', 'color_dodge', 'colorize', 'copy_black', 'copy_blue', 'copy', 'copy_cyan', 'copy_green', 'copy_magenta', 'copy_alpha', 'copy_red', 'copy_yellow', 'darken', 'darken_intensity', 'difference', 'displace', 'dissolve', 'distort', 'divide_dst', 'divide_src', 'dst_atop', 'dst', 'dst_in', 'dst_out', 'dst_over', 'exclusion', 'hard_light', 'hard_mix', 'hue', 'in', 'intensity', 'lighten', 'lighten_intensity', 'linear_burn', 'linear_dodge', 'linear_light', 'luminize', 'mathematics', 'minus_dst', 'minus_src', 'modulate', 'modulus_add', 'modulus_subtract', 'multiply', 'no', 'out', 'over', 'overlay', 'pegtop_light', 'pin_light', 'plus', 'replace', 'saturate', 'screen', 'soft_light', 'src_atop', 'src', 'src_in', 'src_out', 'src_over', 'threshold', 'vivid_light', 'xor', 'stereo', 'freeze', 'interpolate', 'negate', 'reflect', 'soft_burn', 'soft_dodge', 'stamp', 'rmse', 'saliency_blend', 'seamless_blend')¶
(
tuple) The list of composition operators'undefined''alpha'- Only available with ImageMagick-7'atop''blend''blur''bumpmap''change_mask''clear''color_burn''color_dodge''colorize''copy_black''copy_blue''copy''copy_alpha'- Only available with ImageMagick-7'copy_cyan''copy_green''copy_magenta''copy_opacity'- Only available with ImageMagick-6'copy_red''copy_yellow''darken''darken_intensity''difference''displace''dissolve''distort''divide_dst''divide_src''dst_atop''dst''dst_in''dst_out''dst_over''exclusion''freeze'- Added with ImageMagick-7.0.10'hard_light''hard_mix''hue''in''intensity'- Only available with ImageMagick-7'interpolate'- Added with ImageMagick-7.0.10'lighten''lighten_intensity''linear_burn''linear_dodge''linear_light''luminize''mathematics''minus_dst''minus_src''modulate''modulus_add''modulus_subtract''multiply''negate'- Added with ImageMagick-7.0.10'no''out''over''overlay''pegtop_light''pin_light''plus''reflect'- Added with ImageMagick-7.0.10'replace''rmse'- Added with ImageMagick-7.1.0'saliency_blend'- Added with ImageMagick-7.1.1'saturate''screen''seamless_blend'- Added with ImageMagick-7.1.1'soft_burn'- Added with ImageMagick-7.0.10'soft_dudge'- Added with ImageMagick-7.0.10'soft_light''src_atop''src''src_in''src_out''src_over''stamp'- Added with ImageMagick-7.0.10'stereo''threshold''vivid_light''xor'
Changed in version 0.3.0: Renamed from
COMPOSITE_OPStoCOMPOSITE_OPERATORS.Changed in version 0.5.6: Operators have been updated to reflect latest changes in C-API. For ImageMagick-6,
'add'has been renamed to'modulus_add','subtract'has been renamed to'modulus_subtract','divide'has been split into'divide_dst'&'divide_src', and'minus'has been split into'minus_dst'&'minus_src'.See also
- Compositing Images ImageMagick v6 Examples
Image composition is the technique of combining images that have, or do not have, transparency or an alpha channel. This is usually performed using the IM composite command. It may also be performed as either part of a larger sequence of operations or internally by other image operators.
- ImageMagick Composition Operators
Demonstrates the results of applying the various composition composition operators.
- wand.image.COMPRESSION_TYPES = ('undefined', 'b44a', 'b44', 'bzip', 'dxt1', 'dxt3', 'dxt5', 'fax', 'group4', 'jbig1', 'jbig2', 'jpeg2000', 'jpeg', 'losslessjpeg', 'lzma', 'lzw', 'no', 'piz', 'pxr24', 'rle', 'zip', 'zips')¶
(
tuple) The list ofImage.compressiontypes.'undefined''b44a''b44''bzip''dxt1''dxt3''dxt5''fax''group4''jbig1''jbig2''jpeg2000''jpeg''losslessjpeg''lzma''lzw''no''piz''pxr24''rle''zip''zips'
New in version 0.3.6.
Changed in version 0.5.0: Support for ImageMagick-6 & ImageMagick-7
- class wand.image.ChannelDepthDict(image)¶
The mapping table of channels to their depth.
- Parameters:
image (
Image) – an image instance
Note
You don’t have to use this by yourself. Use
Image.channel_depthsproperty instead.New in version 0.3.0.
- class wand.image.ChannelImageDict(image)¶
The mapping table of separated images of the particular channel from the image.
- Parameters:
image (
Image) – an image instance
Note
You don’t have to use this by yourself. Use
Image.channel_imagesproperty instead.New in version 0.3.0.
- exception wand.image.ClosedImageError¶
An error that rises when some code tries access to an already closed image.
- class wand.image.ConnectedComponentObject(cc_object=None)¶
Generic Python wrapper to translate
CCObjectInfostructure into a class describing objects found within an image. This class is generated byImage.connected_components()method.New in version 0.5.5.
Changed in version 0.6.8: Added
keyproperty for ImageMagick 7.1.0- area = None¶
(
numbers.Real) Quantity of pixels that make-up the objects shape.
- center_x = None¶
(
numbers.Real) X offset of objects centroid.
- center_y = None¶
(
numbers.Real) Y offset of objects centroid.
- clone_from_cc_object_info(cc_object)¶
Copy data from
CCObjectInfo.
- clone_from_extra_70A_info(cc_object)¶
Copy the additional values from CCObjectInfo structure. This is the
merge&metricproperties added in ImageMagick 7.0.10.New in version 0.6.3.
- clone_from_extra_710_info(cc_object)¶
Copy additional value from CCObjectInfo structure for properties added to ImageMagick 7.1.0.
New in version 0.6.8.
- height = None¶
(
numbers.Integral) Height of objects minimum bounding rectangle.
- left = None¶
(
numbers.Integral) X offset of objects minimum bounding rectangle.
- merge = None¶
(
bool) Object merge flag. Only available after ImageMagick-7.0.10. ..versionadded:: 0.6.3
- metric = None¶
(
list) List of doubles used by metric. Only available after ImageMagick-7.0.10. ..versionadded:: 0.6.3
- top = None¶
(
numbers.Integral) Y offset of objects minimum bounding rectangle.
- width = None¶
(
numbers.Integral) Width of objects minimum bounding rectangle.
- wand.image.DISPOSE_TYPES = ('undefined', 'none', 'background', 'previous')¶
(
tuple) The list ofBaseImage.disposetypes.'undefined''none''background''previous'
New in version 0.5.0.
- wand.image.DISTORTION_METHODS = ('undefined', 'affine', 'affine_projection', 'scale_rotate_translate', 'perspective', 'perspective_projection', 'bilinear_forward', 'bilinear_reverse', 'polynomial', 'arc', 'polar', 'depolar', 'cylinder_2_plane', 'plane_2_cylinder', 'barrel', 'barrel_inverse', 'shepards', 'resize', 'sentinel', 'rigidaffine')¶
(
tuple) The list ofBaseImage.distort()methods.'undefined''affine''affine_projection''scale_rotate_translate''perspective''perspective_projection''bilinear_forward''bilinear_reverse''polynomial''arc''polar''depolar''cylinder_2_plane''plane_2_cylinder''barrel''barrel_inverse''shepards''resize''sentinel''rigidaffine'- Only available with ImageMagick-7.0.10, or later.
New in version 0.4.1.
- wand.image.DITHER_METHODS = ('undefined', 'no', 'riemersma', 'floyd_steinberg')¶
(
tuple) The list of Dither methods. Used byImage.posterize()andImage.remap()methods.'undefined''no''riemersma''floyd_steinberg'
New in version 0.5.0.
- wand.image.EVALUATE_OPS = ('undefined', 'abs', 'add', 'addmodulus', 'and', 'cosine', 'divide', 'exponential', 'gaussiannoise', 'impulsenoise', 'laplaciannoise', 'leftshift', 'log', 'max', 'mean', 'median', 'min', 'multiplicativenoise', 'multiply', 'or', 'poissonnoise', 'pow', 'rightshift', 'rootmeansquare', 'set', 'sine', 'subtract', 'sum', 'thresholdblack', 'threshold', 'thresholdwhite', 'uniformnoise', 'xor', 'inverse_log')¶
(
tuple) The list of evaluation operators. Used byImage.evaluate()method.'undefined''abs''add''addmodulus''and''cosine''divide''exponential''gaussiannoise''impulsenoise''inverse_log'- Added with ImageMagick-7.0.10-24'laplaciannoise''leftshift''log''max''mean''median''min''multiplicativenoise''multiply''or''poissonnoise''pow''rightshift''set''sine''subtract''sum''threshold''thresholdblack''thresholdwhite''uniformnoise''xor'
See also
- ImageMagick Image Evaluation Operators
Describes the MagickEvaluateImageChannel method and lists the various evaluations operators
- wand.image.FILTER_TYPES = ('undefined', 'point', 'box', 'triangle', 'hermite', 'hanning', 'hamming', 'blackman', 'gaussian', 'quadratic', 'cubic', 'catrom', 'mitchell', 'jinc', 'sinc', 'sincfast', 'kaiser', 'welsh', 'parzen', 'bohman', 'bartlett', 'lagrange', 'lanczos', 'lanczossharp', 'lanczos2', 'lanczos2sharp', 'robidoux', 'robidouxsharp', 'cosine', 'spline', 'sentinel')¶
(
tuple) The list of filter types. Used byImage.resample()andImage.resize()methods.'undefined''point''box''triangle''hermite''hanning''hamming''blackman''gaussian''quadratic''cubic''catrom''mitchell''jinc''sinc''sincfast''kaiser''welsh''parzen''bohman''bartlett''lagrange''lanczos''lanczossharp''lanczos2''lanczos2sharp''robidoux''robidouxsharp''cosine''spline''sentinel'
See also
- ImageMagick Resize Filters
Demonstrates the results of resampling images using the various resize filters and blur settings available in ImageMagick.
- wand.image.FUNCTION_TYPES = ('undefined', 'arcsin', 'arctan', 'polynomial', 'sinusoid')¶
(
tuple) The list ofImage.functiontypes.'undefined''arcsin''arctan''polynomial''sinusoid'
- wand.image.GRAVITY_TYPES = ('forget', 'north_west', 'north', 'north_east', 'west', 'center', 'east', 'south_west', 'south', 'south_east', 'static')¶
(
tuple) The list ofgravitytypes.'forget''north_west''north''north_east''west''center''east''south_west''south''south_east'
New in version 0.3.0.
- class wand.image.HistogramDict(image)¶
Specialized mapping object to represent color histogram. Keys are colors, and values are the number of pixels.
- Parameters:
image (
BaseImage) – the image to get its histogram
New in version 0.3.0.
- wand.image.IMAGE_LAYER_METHOD = ('undefined', 'coalesce', 'compareany', 'compareclear', 'compareoverlay', 'dispose', 'optimize', 'optimizeimage', 'optimizeplus', 'optimizetrans', 'removedups', 'removezero', 'composite', 'merge', 'flatten', 'mosaic', 'trimbounds')¶
(
tuple) The list of methods formerge_layers()andcompare_layers().'undefined''coalesce''compareany'- Only used forcompare_layers().'compareclear'- Only used forcompare_layers().'compareoverlay'- Only used forcompare_layers().'dispose''optimize''optimizeimage''optimizeplus''optimizetrans''removedups''removezero''composite''merge'- Only used formerge_layers().'flatten'- Only used formerge_layers().'mosaic'- Only used formerge_layers().'trimbounds'- Only used formerge_layers().
New in version 0.4.3.
- wand.image.IMAGE_TYPES = ('undefined', 'bilevel', 'grayscale', 'grayscalealpha', 'palette', 'palettealpha', 'truecolor', 'truecoloralpha', 'colorseparation', 'colorseparationalpha', 'optimize', 'palettebilevelalpha')¶
(
tuple) The list of image types'undefined''bilevel''grayscale''grayscalealpha'- Only available with ImageMagick-7'grayscalematte'- Only available with ImageMagick-6'palette''palettealpha'- Only available with ImageMagick-7'palettematte'- Only available with ImageMagick-6'truecolor''truecoloralpha'- Only available with ImageMagick-7'truecolormatte'- Only available with ImageMagick-6'colorseparation''colorseparationalpha'- Only available with ImageMagick-7'colorseparationmatte'- Only available with ImageMagick-6'optimize''palettebilevelalpha'- Only available with ImageMagick-7'palettebilevelmatte'- Only available with ImageMagick-6
See also
- ImageMagick Image Types
Describes the MagickSetImageType method which can be used to set the type of an image
- wand.image.INTERLACE_TYPES = ('undefined', 'no', 'line', 'plane', 'partition', 'gif', 'jpeg', 'png')¶
(
tuple) The list of interlace schemes.'undefined''no''line''plane''partition''gif''jpeg''png'
New in version 0.5.2.
- class wand.image.Image(image=None, blob=None, file=None, filename=None, pseudo=None, background=None, colorspace=None, depth=None, extract=None, format=None, height=None, interlace=None, resolution=None, sampling_factors=None, units=None, width=None)¶
An image object.
- Parameters:
image (
Image) – makes an exact copy of theimageblob (
bytes) – opens an image of theblobbyte arrayfile (file object) – opens an image of the
fileobjectfilename (
basestring) – opens an image of thefilenamestring. Additional Read Modifiers are supported.format (
basestring) – forces filename to buffer.formatto help ImageMagick detect the file format. Used only inbloborfilecaseswidth (
numbers.Integral) – the width of new blank image or an image loaded from raw data.height (
numbers.Integral) – the height of new blank image or an image loaded from raw data.depth (
numbers.Integral) – the depth used when loading raw data.background (
wand.color.Color) – an optional background color. default is transparentresolution (
collections.abc.Sequence,numbers.Integral) – set a resolution value (dpi), useful for vectorial formats (like pdf)colorspace (
basestring) – sets the stack’s default colorspace value before reading any images. SeeCOLORSPACE_TYPES.units (
basestring) – paired withresolutionfor defining an image’s pixel density. SeeUNIT_TYPES.
New in version 0.1.5: The
fileparameter.New in version 0.1.1: The
blobparameter.New in version 0.2.1: The
formatparameter.New in version 0.2.2: The
width,height,backgroundparameters.New in version 0.3.0: The
resolutionparameter.New in version 0.4.2: The
depthparameter.Changed in version 0.4.2: The
depth,widthandheightparameters can be used with thefilename,fileandblobparameters to load raw pixel data.New in version 0.5.0: The
pseudoparameter.Changed in version 0.5.4: Read constructor no longer sets “transparent” background by default. Use the
backgroundparameter to specify canvas color when reading in image.Changed in version 0.5.7: Added the
colorspace&unitsparameter.Changed in version 0.6.3: Added
sampling_factorsparameter for working with YUV streams.- [left:right, top:bottom]
Crops the image by its
left,right,topandbottom, and then returns the cropped one.with img[100:200, 150:300] as cropped: # manipulated the cropped image pass
Like other subscriptable objects, default is 0 or its width/height:
img[:, :] #--> just clone img[:100, 200:] #--> equivalent to img[0:100, 200:img.height]
Negative integers count from the end (width/height):
img[-70:-50, -20:-10] #--> equivalent to img[width-70:width-50, height-20:height-10]
- Returns:
the cropped image
- Rtype:
New in version 0.1.2.
- property animation¶
(
bool) Whether the image is animation or not. It doesn’t only mean that the image has two or more images (frames), but all frames are even the same size. It’s about image format, not content. It’sFalseeven if image/ico consists of two or more images of the same size.For example, it’s
Falsefor image/jpeg, image/gif, image/ico.If image/gif has two or more frames, it’s
True. If image/gif has only one frame, it’sFalse.New in version 0.3.0.
Changed in version 0.3.8: Became to accept image/x-gif as well.
- artifacts = None¶
(
ArtifactTree) A dict mapping to image artifacts. Similar tometadata, but used to alter behavior of various internal operations.New in version 0.5.0.
- blank(width, height, background=None)¶
Creates blank image.
- Parameters:
width (
numbers.Integral) – the width of new blank image.height (
numbers.Integral) – the height of new blank image.background (
wand.color.Color) – an optional background color. default is transparent
- Returns:
blank image
- Return type:
New in version 0.3.0.
- channel_depths = None¶
(
ChannelDepthDict) The mapping of channels to their depth. Read only.New in version 0.3.0.
- channel_images = None¶
(
ChannelImageDict) The mapping of separated channels from the image.with image.channel_images['red'] as red_image: display(red_image)
- clear()¶
Clears resources associated with the image, leaving the image blank, and ready to be used with new image.
New in version 0.3.0.
- close()¶
Closes the image explicitly. If you use the image object in
withstatement, it was called implicitly so don’t have to call it.Note
It has the same functionality of
destroy()method.
- compare_layers(method)¶
Generates new images showing the delta pixels between layers. Similar pixels are converted to transparent. Useful for debugging complex animations.
with img.compare_layers('compareany') as delta: delta.save(filename='framediff_%02d.png')
Note
May not work as expected if animations are already optimized.
- Parameters:
method (
basestring) – Can be'compareany','compareclear', or'compareoverlay'- Returns:
new image stack.
- Return type:
New in version 0.5.0.
- convert(format)¶
Converts the image format with the original image maintained. It returns a converted image instance which is new.
with img.convert('png') as converted: converted.save(filename='converted.png')
- Parameters:
format (
basestring) – image format to convert to- Returns:
a converted image
- Return type:
- Raises:
ValueError – when the given
formatis unsupported
New in version 0.1.6.
Changed in version 0.6.11: Call
MagickSetFormat()method afterMagickSetImageFormat(). This will ensure image info, magick, and filename properties are aligned.
- data_url()¶
Generate a base64 data-url string from the loaded image. Useful for converting small graphics into ASCII strings for HTML/CSS web development.
- Returns:
a data-url formatted string.
- Return type:
basestring
New in version 0.6.3.
- classmethod from_array(array, channel_map=None, storage=None)¶
Create an image instance from a
numpyarray, or any other datatype that implements __array_interface__ protocol.import numpy from wand.image import Image matrix = numpy.random.rand(100, 100, 3) with Image.from_array(matrix) as img: img.save(filename='noise.png')
Use the optional
channel_map&storagearguments to specify the order of color channels & data size. Ifchannel_mapis omitted, this method will will guess"RGB", or"CMYK"based on array shape. Ifstorageis omitted, this method will reference the array’stypestrvalue, and raise aValueErrorif storage-type can not be mapped.Float values must be normalized between 0.0 and 1.0, and signed integers should be converted to unsigned values between 0 and max value of type.
Instances of
Imagecan also be exported to numpy arrays:with Image(filename='rose:') as img: matrix = numpy.array(img)
- Parameters:
array (
numpy.array) – Numpy array of pixel values.channel_map (
basestring) – Color channel layout.storage (
basestring) – Datatype per pixel part.
- Returns:
New instance of an image.
- Return type:
New in version 0.5.3.
Changed in version 0.6.0: Input
arraynow expects theshapeproperty to be defined as`( 'height', 'width', 'channels' )`.
- image_add(image)¶
Copies a given image on to the image stack. By default, the added image will be append at the end of the stack, or immediately after the current image iterator defined by
iterator_set(). Useiterator_reset()before calling this method to insert the new image before existing images on the stack.- Parameters:
image (
Image) – raster to add.
New in version 0.6.7.
- image_get()¶
Generate & return a clone of a single image at the current image-stack index.
New in version 0.6.7.
- image_remove()¶
Remove an image from the image-stack at the current index.
New in version 0.6.7.
- image_set(image)¶
Overwrite current image on the image-stack with given image.
- Parameters:
image (
wand.image.Image) – Wand instance of images to write to stack.
New in version 0.6.7.
- image_swap(i, j)¶
Swap two images on the image-stack.
- Parameters:
i (
numbers.Integral) – image index to replace withjj (
numbers.Integral) – image index to replace withi
New in version 0.6.7.
- make_blob(format=None)¶
Makes the binary string of the image.
- Parameters:
format (
basestring) – the image format to write e.g.'png','jpeg'. it is omittable- Returns:
a blob (bytes) string
- Return type:
- Raises:
ValueError – when
formatis invalid
Changed in version 0.1.6: Removed a side effect that changes the image
formatsilently.New in version 0.1.5: The
formatparameter became optional.New in version 0.1.1.
- property mimetype¶
(
basestring) The MIME type of the image e.g.'image/jpeg','image/png'.New in version 0.1.7.
- montage(font=None, tile=None, thumbnail=None, mode='unframe', frame=None)¶
Generates a new image containing thumbnails if each previous image read.
with Image() as img: for file_path in ['first.png', 'second.png', 'third.png']: with Image(filename=file_path) as item: img.options['label'] = file_path img.image_add(item) style = Font('monospace', 24, 'green') img.montage(font=style, tile='3x1', thumbnail='15x15') img.save(filename='montage.png')
- Parameters:
font (
Font) – Define font style to use when labeling each thumbnail. Thumbnail labeling will only be rendered if'label'value inoptionsdict is defined.tile (
basestring) – The number of thunbnails per rows & column on a page. Example:"6x4".thumbnail (
basestring) – Preferred image size. Montage will attempt to generate a thumbnail to match the geometry. This can also define the border size on each thumbnail. Example:"120x120x+4+3>".mode (
basestring) – Which effect to render. Options include"frame","unframe", and"concatenate". Default"frame".frame (
basestring) – Define ornamental boarder around each thrumbnail. The color of the frame is defined by the image’s matte color. Example:"15x15+3+3".
New in version 0.6.8.
- classmethod ping(file=None, filename=None, blob=None, **kwargs)¶
Ping image header into Image() object, but without any pixel data. This is useful for inspecting image meta-data without decoding the whole image.
- Parameters:
blob (
bytes) – reads an image from theblobbyte arrayfile (file object) – reads an image from the
fileobjectfilename (
basestring) – reads an image from thefilenamestringresolution (
collections.abc.Sequence,numbers.Integral) – set a resolution value (DPI), useful for vector formats (like PDF)format (
basestring) – suggest image file format when reading from ablob, orfileproperty.
New in version 0.5.6.
- profiles = None¶
(
ProfileDict) The mapping of image profiles.New in version 0.5.1.
- pseudo(width, height, pseudo='xc:')¶
Creates a new image from ImageMagick’s internal protocol coders.
- Parameters:
width (
numbers.Integral) – Total columns of the new image.height (
numbers.Integral) – Total rows of the new image.pseudo (
basestring) – The protocol & arguments for the pseudo image.
New in version 0.5.0.
- read(file=None, filename=None, blob=None, background=None, colorspace=None, depth=None, extract=None, format=None, height=None, interlace=None, resolution=None, sampling_factors=None, units=None, width=None)¶
Read new image into Image() object.
- Parameters:
blob (
bytes) – reads an image from theblobbyte arrayfile (file object) – reads an image from the
fileobjectfilename (
basestring) – reads an image from thefilenamestring. Additional Read Modifiers are supported.background (
Color,basestring) – set default background color.colorspace (
basestring) – set default colorspace. SeeCOLORSPACE_TYPES.depth (
numbers.Integral) – sets bits per color sample. Usually8, or16.format (
basestring) – sets which image decoder to read with. Helpful when readingblobdata with ambiguous headers.height (
numbers.Integral) – used withwidthto define the canvas size. Useful for reading image streams.interlace (
basestring) – Defines the interlacing scheme for raw data streams. SeeINTERLACE_TYPES.resolution (
collections.abc.Sequence,numbers.Integral) – set a resolution value (DPI), useful for vectorial formats (like PDF)sampling_factors (
collections.abc.Sequence,basestring) – set up/down stampling factors for YUV data stream. Usually"4:2:2"units (
basestring) – used withresolution, can either be'pixelperinch', or'pixelpercentimeter'.width (
numbers.Integral) – used withheightto define the canvas size. Useful for reading image streams.
New in version 0.3.0.
Changed in version 0.5.7: Added
unitsparameter.Changed in version 0.6.3: Added, or documented, optional pre-read parameters:
background,colorspace,depth,format,height,interlace,sampling_factors, &width.
- reset_sequence()¶
Remove any previously allocated
SingleImageinstances insequenceattribute.New in version 0.6.0.
- save(file=None, filename=None, adjoin=True)¶
Saves the image into the
fileorfilename. It takes only one argument at a time.- Parameters:
file (file object) – a file object to write to
filename (
basestring) – a filename string to write toadjoin (
bool) – write all images to a single multi-image file. Only available if file format supports frames, layers, & etc.
New in version 0.1.1.
Changed in version 0.1.5: The
fileparameter was added.Changed in version 6.0.0: The
adjoinparameter was added.
- classmethod stereogram(left, right)¶
Create a new stereogram image from two existing images.
- See:
Example of Stereogram.
- Parameters:
left (
wand.image.Image) – Left-eye image.right (
wand.image.Image) – Right-eye image.
New in version 0.5.4.
- class wand.image.ImageProperty(image)¶
The mixin class to maintain a weak reference to the parent
Imageobject.New in version 0.3.0.
- property image¶
(
Image) The parent image.It ensures that the parent
Image, which is held in a weak reference, still exists. Returns the dereferencedImageif it does exist, or raises aClosedImageErrorotherwise.- Exc:
ClosedImageError when the parent Image has been destroyed
- class wand.image.Iterator(image=None, iterator=None)¶
Row iterator for
Image. It shouldn’t be instantiated directly; instead, it can be acquired throughImageinstance:assert isinstance(image, wand.image.Image) iterator = iter(image)
It doesn’t iterate every pixel, but rows. For example:
for row in image: for col in row: assert isinstance(col, wand.color.Color) print(col)
Every row is a
collections.abc.Sequencewhich consists of one or morewand.color.Colorvalues.- Parameters:
image (
Image) – the image to get an iterator
New in version 0.1.3.
- c_clear_exception = wand.api.library.PixelClearIteratorException¶
(
ctypes.CFUNCTYPE) Thectypesfunction that clears an exception of theresource.Note
It is an abstract attribute that has to be implemented in the subclass.
- c_destroy_resource = wand.api.library.DestroyPixelIterator¶
(
ctypes.CFUNCTYPE) Thectypesfunction that destroys theresource.Note
It is an abstract attribute that has to be implemented in the subclass.
- c_get_exception = wand.api.library.PixelGetIteratorException¶
(
ctypes.CFUNCTYPE) Thectypesfunction that gets an exception from theresource.Note
It is an abstract attribute that has to be implemented in the subclass.
- c_is_resource = wand.api.library.IsPixelIterator¶
(
ctypes.CFUNCTYPE) Thectypespredicate function that returns whether the given pointer (that contains a resource data usually) is a valid resource.Note
It is an abstract attribute that has to be implemented in the subclass.
- clone()¶
Clones the same iterator.
- next(x=None)¶
Return the next item from the iterator. When exhausted, raise StopIteration
- wand.image.KERNEL_INFO_TYPES = ('undefined', 'unity', 'gaussian', 'dog', 'log', 'blur', 'comet', 'binomial', 'laplacian', 'sobel', 'frei_chen', 'roberts', 'prewitt', 'compass', 'kirsch', 'diamond', 'square', 'rectangle', 'octagon', 'disk', 'plus', 'cross', 'ring', 'peaks', 'edges', 'corners', 'diagonals', 'line_ends', 'line_junctions', 'ridges', 'convex_hull', 'thin_se', 'skeleton', 'chebyshev', 'manhattan', 'octagonal', 'euclidean', 'user_defined')¶
(
tuple) The list of builtin kernels.'undefined''unity''gaussian''dog''log''blur''comet''laplacian''sobel''frei_chen''roberts''prewitt''compass''kirsch''diamond''square''rectangle''octagon''disk''plus''cross''ring''peaks''edges''corners''diagonals''line_ends''line_junctions''ridges''convex_hull''thin_se''skeleton''chebyshev''manhattan''octagonal''euclidean''user_defined''binomial'
- wand.image.MORPHOLOGY_METHODS = ('undefined', 'convolve', 'correlate', 'erode', 'dilate', 'erode_intensity', 'dilate_intensity', 'iterative_distance', 'open', 'close', 'open_intensity', 'close_intensity', 'smooth', 'edgein', 'edgeout', 'edge', 'tophat', 'bottom_hat', 'hit_and_miss', 'thinning', 'thicken', 'distance', 'voronoi')¶
(
tuple) The list of morphology methods.'undefined''convolve''correlate''erode''dilate''erode_intensity''dilate_intensity''distance''open''close''open_intensity''close_intensity''smooth''edgein''edgeout''edge''tophat''bottom_hat''hit_and_miss''thinning''thicken''voronoi''iterative_distance'
- class wand.image.Metadata(image)¶
Class that implements dict-like read-only access to image metadata like EXIF or IPTC headers. Most WRITE encoders will ignore properties assigned here.
- Parameters:
image (
Image) – an image instance
Note
You don’t have to use this by yourself. Use
Image.metadataproperty instead.New in version 0.3.0.
- wand.image.NOISE_TYPES = ('undefined', 'uniform', 'gaussian', 'multiplicative_gaussian', 'impulse', 'laplacian', 'poisson', 'random')¶
(
tuple) The list of noise types used byImage.noise()method.'undefined''uniform''gaussian''multiplicative_gaussian''impulse''laplacian''poisson''random'
New in version 0.5.3.
- wand.image.ORIENTATION_TYPES = ('undefined', 'top_left', 'top_right', 'bottom_right', 'bottom_left', 'left_top', 'right_top', 'right_bottom', 'left_bottom')¶
(
tuple) The list oforientationtypes.New in version 0.3.0.
- class wand.image.OptionDict(image)¶
Free-form mutable mapping of global internal settings.
New in version 0.3.0.
Changed in version 0.5.0: Remove key check to
OPTIONS. Image properties are specific to vendor, and this library should not attempt to manage the 100+ options in a whitelist.
- wand.image.PAPERSIZE_MAP = {'10x13': (720, 936), '10x14': (720, 1008), '11x17': (792, 1224), '2A0': (3370, 4768), '4A0': (4768, 6741), '4x6': (288, 432), '5x7': (360, 504), '7x9': (504, 648), '8x10': (576, 720), '9x11': (648, 792), '9x12': (648, 864), 'a0': (2384, 3370), 'a1': (1684, 2384), 'a10': (74, 105), 'a2': (1191, 1684), 'a3': (842, 1191), 'a4': (595, 842), 'a4small': (595, 842), 'a5': (420, 595), 'a6': (298, 420), 'a7': (210, 298), 'a8': (147, 210), 'a9': (105, 147), 'archC': (1296, 1728), 'archa': (648, 864), 'archb': (864, 1296), 'archd': (1728, 2592), 'arche': (2592, 3456), 'b0': (2920, 4127), 'b1': (2064, 2920), 'b10': (91, 127), 'b2': (1460, 2064), 'b3': (1032, 1460), 'b4': (729, 1032), 'b5': (516, 729), 'b6': (363, 516), 'b7': (258, 363), 'b8': (181, 258), 'b9': (127, 181), 'c0': (2599, 3676), 'c1': (1837, 2599), 'c2': (1298, 1837), 'c3': (918, 1296), 'c4': (649, 918), 'c5': (459, 649), 'c6': (323, 459), 'c7': (230, 323), 'csheet': (1224, 1584), 'dsheet': (1584, 2448), 'esheet': (2448, 3168), 'executive': (540, 720), 'flsa': (612, 936), 'flse': (612, 936), 'folio': (612, 936), 'halfletter': (396, 612), 'isob0': (2835, 4008), 'isob1': (2004, 2835), 'isob10': (88, 125), 'isob2': (1417, 2004), 'isob3': (1001, 1417), 'isob4': (709, 1001), 'isob5': (499, 709), 'isob6': (354, 499), 'isob7': (249, 354), 'isob8': (176, 249), 'isob9': (125, 176), 'jisb0': (1030, 1456), 'jisb1': (728, 1030), 'jisb2': (515, 728), 'jisb3': (364, 515), 'jisb4': (257, 364), 'jisb5': (182, 257), 'jisb6': (128, 182), 'ledger': (1224, 792), 'legal': (612, 1008), 'letter': (612, 792), 'lettersmall': (612, 792), 'monarch': (279, 540), 'quarto': (610, 780), 'statement': (396, 612), 'tabloid': (792, 1224)}¶
(
dict) Map of papersize names to page sizes. Each page size is a width & heighttupleat a 72dpi resolution.from wand.image import Image, PAPERSIZE_MAP w, h = PAPERSIZE_MAP["a4"] with Image(width=w, height=h, background="white") as img: img.save(filename="a4_page.png")
New in version 0.6.4.
- wand.image.PIXEL_INTERPOLATE_METHODS = ('undefined', 'average', 'average9', 'average16', 'background', 'bilinear', 'blend', 'catrom', 'integer', 'mesh', 'nearest', 'spline')¶
(
tuple) List of interpolate pixel methods (ImageMagick-7 only.)'undefined''average''average9''average16''background''bilinear''blend''catrom''integer''mesh''nearest''spline'
New in version 0.5.0.
- class wand.image.ProfileDict(image)¶
The mapping table of embedded image profiles.
Use this to get, set, and delete whole profile payloads on an image. Each payload is a raw binary string.
For example:
with Image(filename='photo.jpg') as img: # Extract EXIF with open('exif.bin', 'wb') as payload: payload.write(img.profiles['exif']) # Import ICC with open('color_profile.icc', 'rb') as payload: img.profiles['icc'] = payload.read() # Remove XMP del imp.profiles['xmp']
See also
Embedded Image Profiles for a list of supported profiles.
New in version 0.5.1.
- wand.image.RENDERING_INTENT_TYPES = ('undefined', 'saturation', 'perceptual', 'absolute', 'relative')¶
(
tuple) List of rendering intent types used forImage.rendering_intentproperty.'undefined''saturation''perceptual''absolute''relative'
New in version 0.5.4.
- wand.image.SPARSE_COLOR_METHODS = {'barycentric': 1, 'bilinear': 7, 'inverse': 19, 'manhattan': 20, 'shepards': 16, 'undefined': 0, 'voronoi': 18}¶
(
tuple) List of sparse color methods used byImage.sparse_color()'undefined''barycentric''bilinear''shepards''voronoi''inverse''manhattan'
New in version 0.5.3.
- wand.image.STATISTIC_TYPES = ('undefined', 'gradient', 'maximum', 'mean', 'median', 'minimum', 'mode', 'nonpeak', 'root_mean_square', 'standard_deviation')¶
(
tuple) The list of statistic types used byImage.statistic().'undefined''gradient''maximum''mean''median''minimum''mode''nonpeak''root_mean_square''standard_deviation'
New in version 0.5.3.
- wand.image.STORAGE_TYPES = ('undefined', 'char', 'double', 'float', 'integer', 'long', 'quantum', 'short')¶
(
tuple) The list of pixel storage types.'undefined''char''double''float''integer''long''quantum''short'
New in version 0.5.0.
- wand.image.UNIT_TYPES = ('undefined', 'pixelsperinch', 'pixelspercentimeter')¶
(
tuple) The list of resolution unit types.'undefined''pixelsperinch''pixelspercentimeter'
See also
- ImageMagick Image Units
Describes the MagickSetImageUnits method which can be used to set image units of resolution
- wand.image.VIRTUAL_PIXEL_METHOD = ('undefined', 'background', 'dither', 'edge', 'mirror', 'random', 'tile', 'transparent', 'mask', 'black', 'gray', 'white', 'horizontal_tile', 'vertical_tile', 'horizontal_tile_edge', 'vertical_tile_edge', 'checker_tile')¶
(
tuple) The list ofvirtual_pixeltypes.'undefined''background''constant'- Only available with ImageMagick-6'dither''edge''mirror''random''tile''transparent''mask''black''gray''white''horizontal_tile''vertical_tile''horizontal_tile_edge''vertical_tile_edge''checker_tile'
New in version 0.4.1.
- wand.image.manipulative(function)¶
Mark the operation manipulating itself instead of returning new one.